Fig. 1.
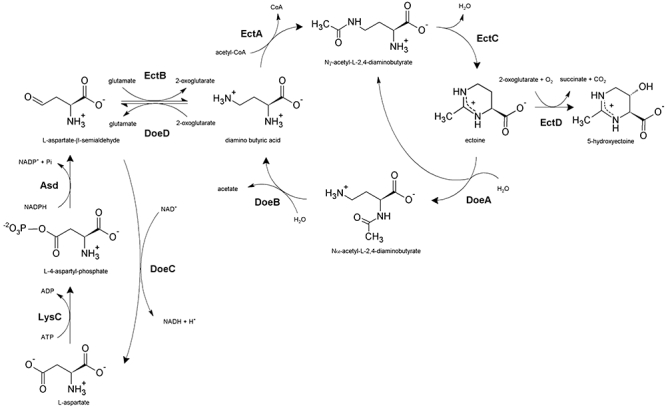
Metabolic pathway of the compatible solute ectoine in H. elongata. The degradation pathway is based on genetic and chromatographic analysis carried out in this study. Shown here is the hydrolysis of ectoine that leads directly to Nγ- and Nα-acetyl-l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid. For more details on DoeA activity see text. The depicted ectoine biosynthesis pathway is according to studies previously published (Peters et al., 1990; Göller et al., 1998; Ono et al., 1999). LysC: aspartate kinase; Asd: β-aspartate-semialdehyde-dehydrogenase; EctB: l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid transaminase; EctA: l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid Nγ-acetyltransferase; EctC: ectoine synthase; EctD: ectoine hydroxylase; DoeA: ectoine hydrolase; DoeB: Nα-acetyl-l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid deacetylase; DoeD: l-2,4-diaminobutyric acid transaminase; DoeC: aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase.
