Fig. 5.
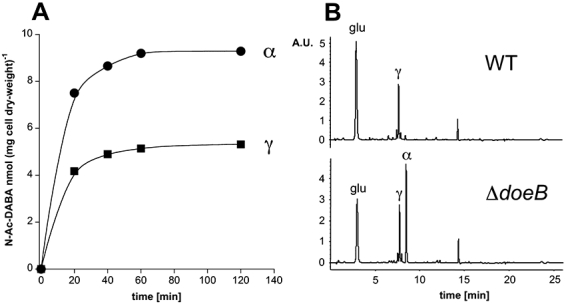
Chromatographic analysis of the cytoplasm from (A) E. coli expressing recombinant doeA and (B) H. elongata wild type and ΔdoeB-mutant strain KB42.A. Time course of Nα-Ac-DABA and Nγ-Ac-DABA formation from ectoine in E. coli expressing recombinant doeA. Cells were grown in mineral salt medium containing 340 mM NaCl. Ectoine was added (1 mM) and the cytoplasmic Nα-Ac-DABA (α) and Nγ-Ac-DABA (γ) content was determined by OPA-HPLC shortly before and 20, 40, 60 and 120 min after ectoine was added. Data presented are the mean from two independent experiments. No N-Ac-DABA was formed in E. coli cells without doeA.B. Chromatogram of the cytoplasm from H. elongata KB42 (ΔdoeB) and wild-type cells (WT), which were grown on mineral salt medium (1.03 M NaCl) in the presence of 500 µM glucose and 10 mM ectoine. After depletion of carbon-source glucose, the amino acid content of both strains was determined by OPA-HPLC. In wild-type cells glutamate (glu) and the ectoine precursor Nγ-Ac-DABA (γ) are detectable. In ΔdoeB mutant strain KB42 Nα-Ac-DABA (α) is accumulated as the predominant amino-reactive solute. Similar results were obtained when ectoine degradation was induced by hypoosmotic shock diluting the medium from 1.03 M down to 0.51 M NaCl. A.U., arbitrary units.
