Figure 1.
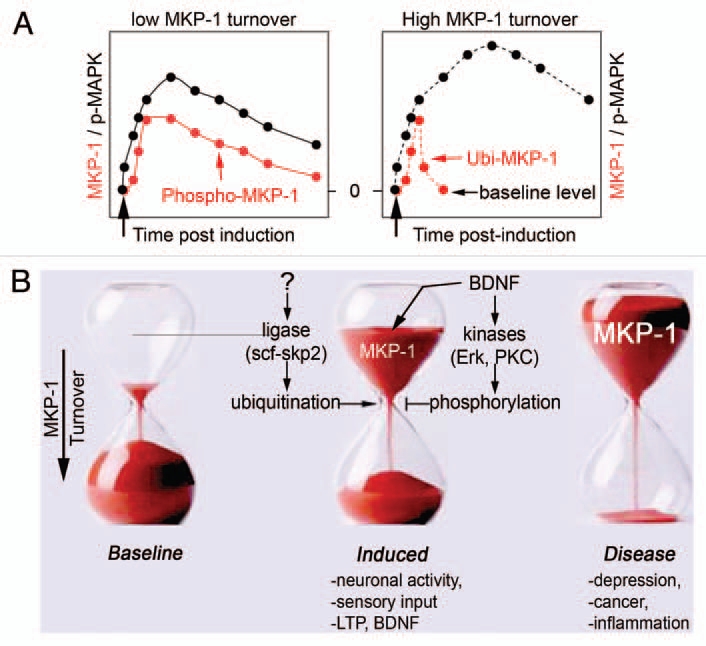
Control of MKP-1 levels. (A) Baseline expression of MKP-1 is low, but highly inducible by sensory stimuli, neuronal activity and trophic factors such as BDNF. Once expressed, MKP-1 is unstable with a turnover <1 h. When phosphorylated by neuronal activity or BDNF, MKP-1 stability extends to >8 h.1 As a consequence, MAPK signaling is shaped accordingly to MKP-1 levels. (B) The mechanisms that regulate MKP-1 levels involve protein kinases and ubiquitin ligases. Abnormal expression of MKP-1 is a hallmark of several disorders, such as stress and depression.2
