Fig. 2.
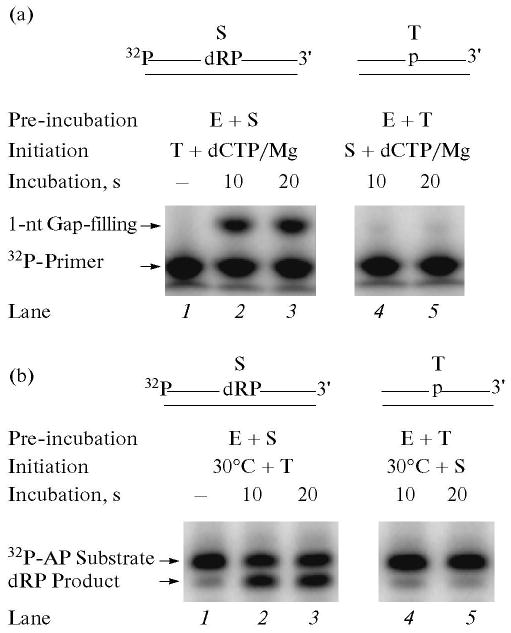
Gap-filling DNA synthesis and removal of the dRP group by polymerase β in the presence of a DNA trap. Schematic representations of 32P-labeled DNA substrate (S) and a DNA trap (T) are illustrated above the phosphorimage of the gels. E denotes polymerase β. (a) Gap-filling DNA synthesis by polymerase β in the presence of a DNA trap was examined. The reaction mixture was assembled on ice, either with 60 nM polymerase β and 20 nM 5′-end 32P-labeled UDG/APE1-treated DNA (lanes 1–3), or with polymerase β and DNA trap (lanes 4, 5). Reactions were initiated by temperature jump and the addition of a mixture of dCTP, DNA trap, and MgCl2 (lanes 1–3), or dCTP, 32P-labeled UDG/APE1-treated DNA, and MgCl2 (lanes 4, 5), respectively. Samples were withdrawn at 10 and 20 s and analyzed. The positions of the 32P-labeled primer and 1-nt gap-filling product are indicated. (b) For analyzing the dRP lyase activity of polymerase β in the presence of a DNA trap, the reaction mixture was assembled on ice, either with 60 nM polymerase β and 20 nM 3′-end 32P-labeled UDG/APE1-treated DNA (lanes 1–3), or polymerase β and the trap (lanes 4, 5). Reactions were initiated by temperature jump and addition of a DNA trap (lanes 1–3) or 32P-labeled substrate (lanes 4, 5), respectively. Samples were withdrawn at 10 and 20 s. The reaction products were stabilized by the addition of NaBH4, and the reaction products were analyzed. The positions of the 32P-labeled dRP substrate and the product are indicated.
