Fig. 3.
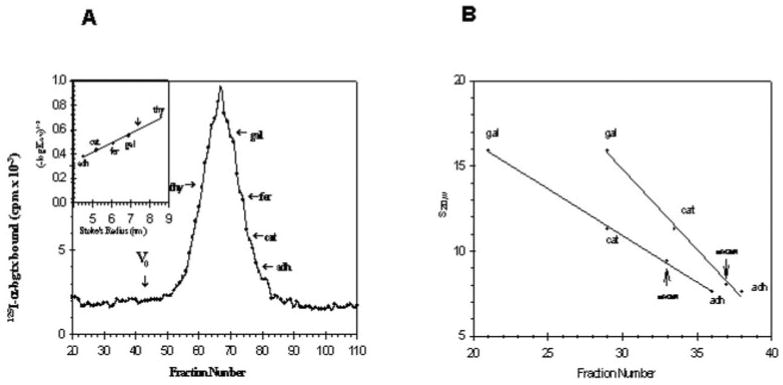
A, determination of Stoke's radius of purified receptor. Gel filtration of the purified receptor is shown. Purified receptor and marker proteins were applied to a column (1 × 50 cm) of Separose 4B as described under “Materials and Methods.” The flow rate was 7.5 ml/h, and 400-μl fractions were collected. The void volume V0 of the column was determined using blue dextran. Specific binding of 125I-α-bungarotoxin to aliquots to each fraction was determined with the DEAE filter assay. thy, thyroglobulin; gal, β-galactosidase; fer, ferritin; cat, catalase, adh, alcohol dehydrogenase). The inset shows the data plotted according to Siegel and Monty (40). The vertical arrow marks the position of the peak of the purified binding protein. B, determination of the apparent s20,w values for the receptor protein in H2O and D2O. Linear sucrose gradients (5–20%) were prepared in H2O and D2O containing 10 mm NaPi, pH 7.3, 500 mm NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, 1 mm EDTA, 3 mm NaN3. 200 μl of sample containing protease inhibitors was loaded onto 4.8 ml of gradient. Centrifugation was carried out in a Beckman SW 50.1 rotor at 50,000 rpm for 5 h at 4 °C. After centrifugation 100-μl fractions were collected. Aliquots of each fractions were used to determine the peaks of α-bungarotoxin binding activity and internal standards. The vertical arrows indicate the peak of α-bungarotoxin binding activity. The internal standards used were β-galactosidase (s20,w = 15.9), bovine liver catalase (s20,w = 11.3), and yeast alcohol dehydrogenase (s20,w = 7.6).
