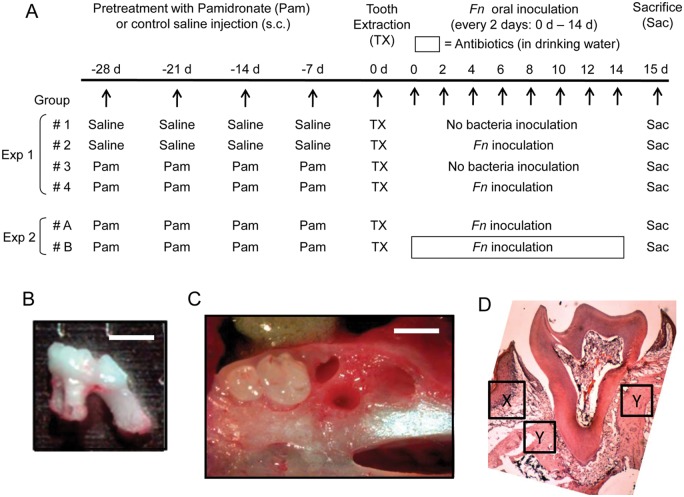
Figure 1.
Study design for in vivo experiment to induce BONJ-like lesion. (A) Experiment 1 (Exp 1). To examine the effects of Pam and Fn on the development BONJ-like lesions, we divided the mice into 4 groups (n = 10/group) as described in the “Materials & Methods” section: (Group 1) saline (control), (Group 2) Fn, (Group 3) Pam alone, and (Group 4) Pam+Fn. To Groups 3 and 4, Pam (1 mg/kg/wk in saline) was subcutaneously (s.c.) injected weekly for 4 wks prior to tooth extraction (-28, -21, -14, and -7 days). Group 1 (saline) and Group 2 (Fn) received control saline injection (s.c.) instead of Pam, following the same injection schedule as Pam (-28, -21, -14, and -7 days). On Day 0, the first right maxillary molar was extracted under anesthesia (ketamine/xylazine) without causing fracture in alveolar bone or tooth (B, C). After tooth extraction, each animal in Group 2 (Fn) or Group 4 (Pam+Fn) was inoculated orally with live Fn (109 CFU/50 µL PBS with 5% carboxymethyl cellulose/animal) every other day until termination of the experiment scheduled at Day 15. Experiment 2 (Exp 2). For examination of the effects of antibiotics on the BONJ-like lesions induced by Pam+Fn, both Group A (n = 10; Pam+Fn) and Group B (n = 10; Pam+Fn) received Pam injection (1 mg/kg/wk in saline s.c.) weekly for 4 wks prior to tooth extraction (-28, -21, -14, and -7 days). After tooth extraction, both groups received oral inoculation with live Fn (109 CFU) every other day until termination of the experiment scheduled at Day 15. After tooth extraction until termination (Day 0 to Day 15), Group A animals were supplied with control regular drinking water, while Group B received drinking water containing an antibiotic cocktail, consisting of ampicillin (1 g/L), metronidazole (1 g/L), vancomycin (0.5 g/L), and neomycin sulfate (1 g/L). (B) Image of extracted maxillary first molar is shown. (C) Image of extraction socket is shown. Soft tissue was removed so that structure of alveolar bone can be visualized. Bar = 1 mm. (D) Histological image (H&E staining) of first right maxillary molar of control mice receiving no treatment is shown. The specific location and area where gingival epithelium, connective tissue, and bone were evaluated in Fig. 3 as well as Appendix Fig. 4 are indicated by “X” (gingival epithelium and connective tissue) and “Y” (bone), respectively.