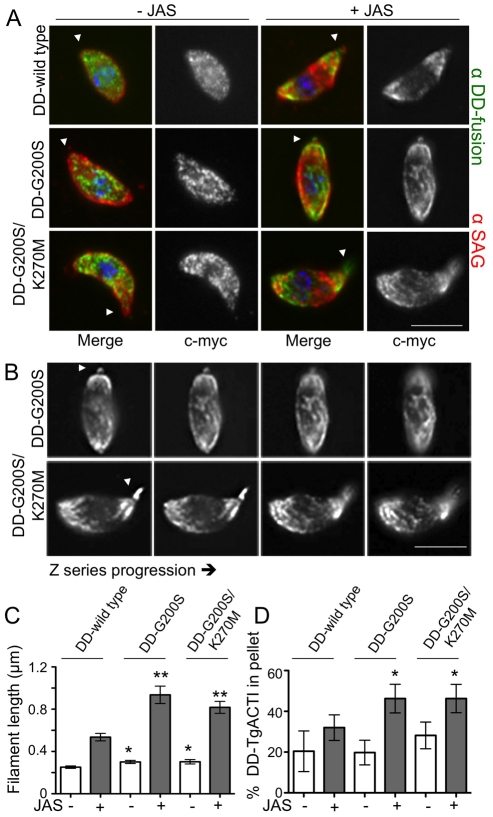
Figure 9. Stabilized actin alleles are more sensitive to JAS-stabilization than endogenous TgACTI in Toxoplasma.
(A) Localization of c-myc-tagged DD-TgACTI alleles in parasites treated with Shield-1 for 40 hr as visualized by immunofluorescence with anti-c-myc antibody (green) and SAG1 (red). Treatment with low levels of JAS (i.e. 0.25 µM) induced spiral patterns of filaments in parasites expressing stabilized actin alleles (right). Apical end noted with arrowhead. Scale bar, 5 µm. (B) Images from (A) shown as z-slices (∼0.3 µm). Actin spirals in JAS-treated parasites were visualized by staining with anti-c-myc antibody. Apical end noted with arrowhead. Scale bar, 5 µm. (C) Quantitation of length of actin puncta and spirals formed in individual parasites treated with ±0.25 µM JAS. Mean ± S.D. * P<0.05 ** P<0.005 (Student's t-test) vs. DD-wild type with same JAS treatment. (D) Sedimentation analysis of F actin in parasites expressing DD-TgACTI fusions and treated ± Shield-1 for 40 hr. Cell lysates were prepared ±0.5 µM JAS, sedimented for 1 hr at 350,000g and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and quantitative Western blotting. Mean ± S.D., n = 3 experiments. * P<0.05 (Student's t-test) vs. DD-wild type.