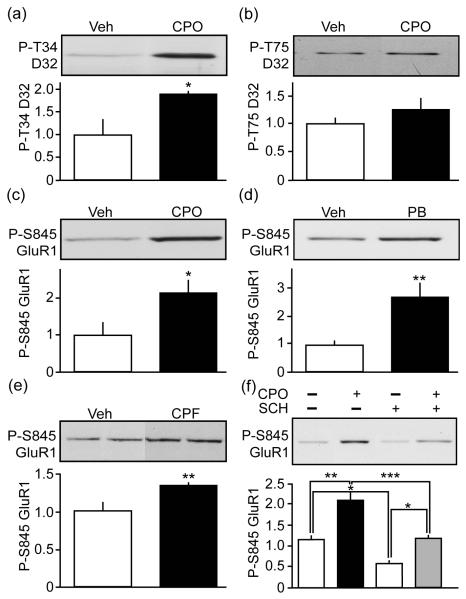
Fig. 1.
Chlorpyrifos and pyridostigmine bromide activate PKA signaling in striatum. Effects of treatment of mouse striatal slices with CPO (100 μM, 60 min) on DARPP-32 (D32) phosphorylation by (a) PKA at Thr34 (P-T34) or (b) Cdk5 at Thr75 (P-T75) vs. vehicle (Veh) are shown as representative blots with quantification. The effects of treatment of CPO (c) or PB (d) (100 μM, 60 min) on GluR1 phosphorylation at Ser845 (P-S845) is shown. (e) The effect of systemic exposure to CPF on striatal P-S845 GluR1 is shown. (f) Effects of treatment of mouse striatal slices with CPO (100 μM, 60 min) on P-S845 GluR1 in the absence (−) and presence (+) of the D1 receptor antagonist SCH23390 (SCH, 1 μM). Data represent means ± SEM normalized for total levels. *p=0.0298, Student’s t-test, for a, n=3. *p=0.0305, Student’s t-test, for c, n=4. **p=0.0100, Student’s t-test, for d, n=4-5. **p=0.0085, Student’s t-test, for e, n=5. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ANOVA with Newman-Keuls post-hoc test, for f, n=3-4.