Fig. 3.
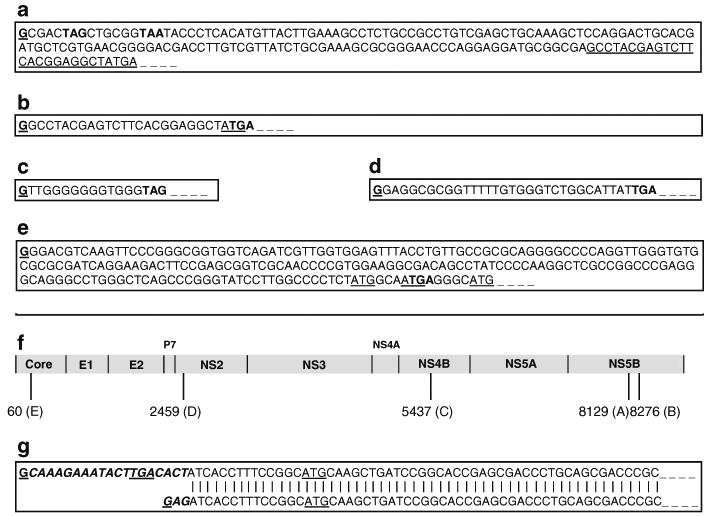
Sequencing of the 5′ ends of the truncated transgene RNAs by 5′ RACE revealed alternate transcription starts within the HCV ORF. a 5′ nucleotide sequence of the longer mRNA transcript (presumably 1.6 kb) with the transcription start site in the middle of the NS5B region. Underlined bases are the beginning of the sequence b. b 5′ nucleotide sequence of the mRNA transcript, shorter by 147 bases as compared to (a) above, with the transcription start site also in the middle of the NS5B region. Note that the first G of this sequence is the 147th base of the above. c 5′ nucleotide sequence of the mRNA transcript (presumably 4.4 kb) with transcription start site in the NS4B region. d 5′ nucleotide sequence of the longest mRNA transcript (presumably 7.6 kb) from an unrecombined Alb-NS transgene and a NS-derived transcript from the FL-N/35 line. e 5′ nucleotide sequence of the longest mRNA transcript (predicted size, 9 kb, and undetectable on northern) from an FL-N/35 tg liver. All five mRNA species begin with a nontemplate-specific 5′ G base and appear to be capped. Stop codons are indicated in boldface triplets, in Fig. 3a–e. f HCV map (genotype 1b) showing nucleotide positions of the alternate transcription start sites along the HCV ORF represented by the above sequences. g Trans-splicing of the Alb-NS transcript. Upper sequence: Actual nucleotide sequence of the Alb-NS transgene mRNA, which includes the upstream spliced leader sequence that ends in a 5′ G base and appears to be capped. Note that the spliced leader sequence contains a potential stop codon (TGA). Lower sequence: Predicted nucleotide sequence of a recombined Alb-NS transgene mRNA containing a splice acceptor (AG) site at its 5′ end and a hypothetical G cap preceding it
