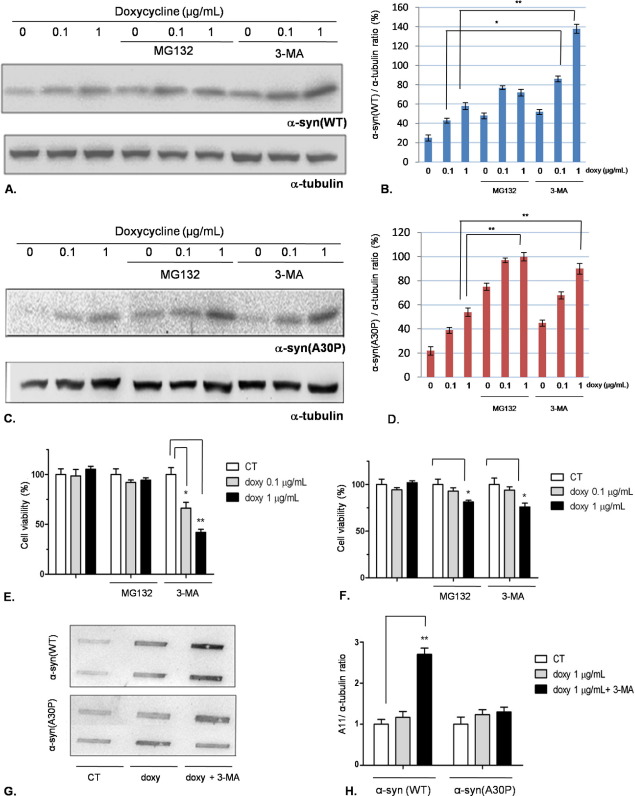
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of macroautophagy by 3-MA leads to α-syn(WT) accumulation, toxicity, and oligomer formation in PC12/TetOn. (A) PC12/TetOn cells expressing α-syn(WT) were exposed to 0.1 or 1 μg/ml of doxycycline for 48 h, and then the UPS inhibitor MG132 or the macroautophagy inhibitor 3-MA was added for further 18 h. Alpha-syn(WT) expression level was then quantified by Western blotting, using α-tubulin as internal standard. The blot quantification (three replicates for each condition) is shown in (B). **: P<0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. (C) The same experiment was carried out using PC12/TetOn overexpressing α-syn(A30P). The graph shown in (D) reports the quantification by densitometric analysis (three replicates for each condition). **: P<0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. (E) Cell viability assessment for the PC12/TetOn cells expressing α-syn(WT). The experimental scheme was the same described in (A). *: P<0.05; **P<0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. (F) Cell viability assay for PC12/TetOn cells expressiong α-syn(A30P) after doxycycline stimulation. The experiment was carried out as detailed in (A); *: P<0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post-hoc test. (G) Representative dot blot showing the effect of 3-MA treatment on α-syn oligomer formation detected by A11 antibody. PC12/TetOn cells were incubated with doxycycline (1 μg/ml) for 48 h, and then 3-MA 10 mM was added for further 18 h. Oligomeric species formation was assessed by A11 reactivity. The bar graph in (H) shows the densitometric quantification of three independent replicates, performed by normalizing the A11 signal to α-tubulin immunoreactivity in the same blot (not shown). For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.