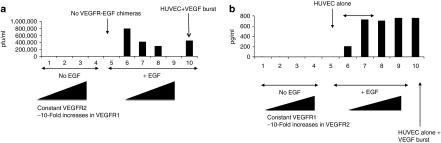
Figure 3.
Crosstalk between VEGFR1 and VEGR2 signaling in human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC). (a) HUVEC/EGF-VEGFR2 cells were grown in the absence of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), with no endothelial growth factor (EGF) burst (columns 1–4), or with EGF burst (columns 5–10), and subsequent reovirus infection. The cells transduced with EGF-VEGFR2 were either mock infected (columns 1 and 6) or were infected with 10-fold increasing levels of EGF-VEGFR1 virus at levels of 1 µl (columns 2 and 7), 10 µl (columns 3 and 8) or 100 µl (columns 4 and 9) of virus supernatants. Column 5, HUVEC alone, not transduced with EGF-VEGFR1 or 2 chimeric receptors, grown in the absence of VEGF; column 10, HUVEC alone deprived of VEGF for 48 hours then given a VEGF burst and subsequent reovirus infection. Reoviral titers shown are the mean of duplicate wells per treatment and the data are representative of four different experiments. (b) HUVEC/EGF-VEGFR1 cells were grown in the absence of VEGF, with no EGF burst (columns 1–4), or with EGF burst (columns 5–10), subsequent reovirus infection and addition of RL2 NK cells as described in Figure 2a. HUVEC/EGF-VEGFR1 cultures were either mock infected (columns 1 and 6) or were infected with 10-fold increasing levels of EGF-VEGFR2 virus at levels of 1 µl (columns 2 and 7), 10 µl (columns 3 and 8) or 100 µl (columns 4 and 9) of virus supernatants. Column 5, HUVEC alone, not transduced with EGF-VEGFR1 or 2 chimeric receptors, grown in the absence of VEGF. Column 10, HUVEC alone deprived of VEGF for 48 hours then given a VEGF burst and subsequent reovirus/NK treatment. Reoviral titers shown are the mean of duplicate wells per treatment and the data are representative of three different experiments.