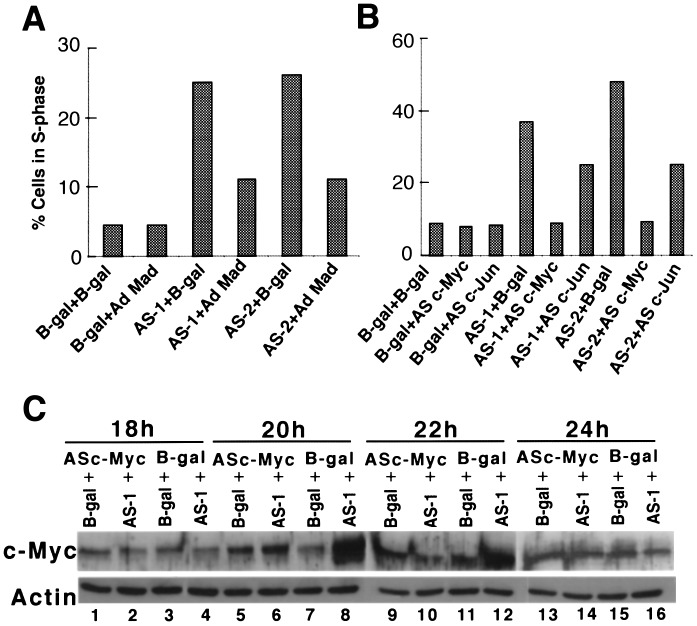
Figure 5.
Reversal of p300 depletion-dependent premature S phase induction. (A) Inhibition of premature S phase induction in p300-depleted MCF10A cells by overexpression of MAD. Serum-starved MCF10A cells were coinfected with AS Ad vectors at 200 pfu/cell with or without Ad-MAD (100 pfu/cell), which expresses MAD protein. Ad-β-gal was always used to maintain the multiplicity of infection uniform in all experiments. (B) Reversal of early S phase entry in p300-depleted cells. Serum-starved MCF10A cells were coinfected with either AS p300 sequences and AS-c-Myc or AS-c-Jun. Ad-β-gal was used to maintain the multiplicity of infection. (C) Inhibition of c-MYC protein synthesis in p300 depleted cells. Serum-starved MCF10A cells were coinfected with different adenoviral vectors in combinations as indicated below. In lanes 1, 5, 9, and 13 Ad-β-gal was mixed with AS-c-Myc; in lanes 2, 6, 10, and 14 AS-1 was mixed with AS-c-Myc; in lanes 3, 7, 11, and 15 Ad-β-gal was mixed with Ad -β-gal and in lanes 4, 8, 12, and 16, Ad-β-gal was mixed with AS-1. Protein lysates obtained from these cells at different periods of infection were assayed for c-MYC protein levels by Western blot analysis. Western blot membrane shown (Upper) was reprobed with α-actin antibody.