Figure 2.
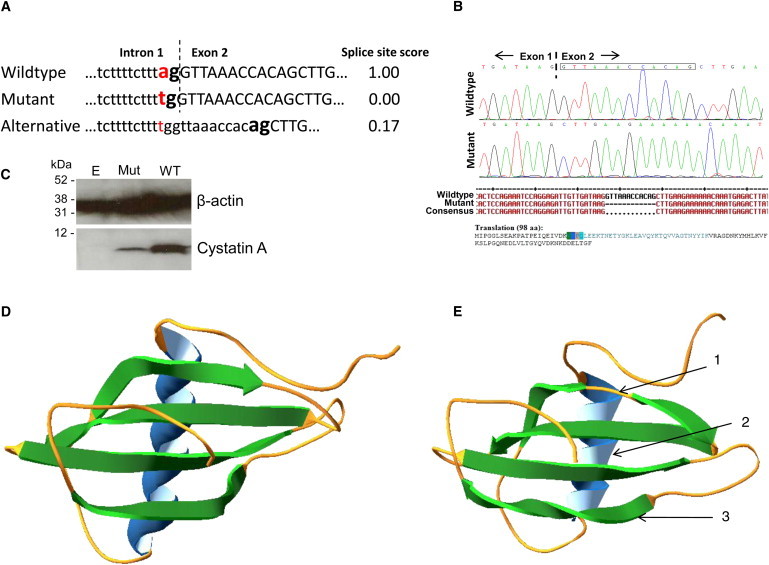
Evaluation of the c.67-2A>T Mutant Cystatin A
(A) With the Neural Network Splice Site Prediction software18 the WT CSTA splice-site scores a maximum score of 1, whereas the mutated splice site, c.67-2A>T, is predicted to score 0. A predicted alternative splice site that is 12 bp into exon 2 has a very weak score of 0.17.
(B) An in vitro splice assay showed that in the presence of the c.67-2A>T mutation, the splicing machinery uses an alternative splice site that leads to skipping of the first 12 bp of exon 2 of CSTA (boxed nucleotides on sequence trace), predicted to result in an in-frame deletion of the four amino acids: Val-Lys-Pro-Gln (residues 23-26) in the cystatin A protein.
(C) Immunoblotting of lysates collected from HEK293T cells transfected with empty pcDNA3 vector, the mutant CSTA minigene construct with the c.67-2A>T splice-site change (Mut), and the WT CSTA minigene construct showed greatly reduced levels of expression from the mutant construct, probably because of utilization of the much weaker splice-acceptor site within exon 2.
(D) In silico modeling shows the predicted ribbon structure of WT cystatin A.
(E) In silico modeling of the splice-site mutant, c.67-2A>T, cystatin A with the four amino acid deletion; the model shows the possible structural differences between the mutant and WT proteins: (1) the first β sheet is split by a random coil giving two shorter β sheets, (2) the α-helix has lost one complete turn and changed its orientation, and (3) the fourth β sheet has a second twist. Structures determined from amino acid sequence with i-Tasser online server29 and figures produced with Swiss-PdbViewer 4.0.30
