Figure 5.
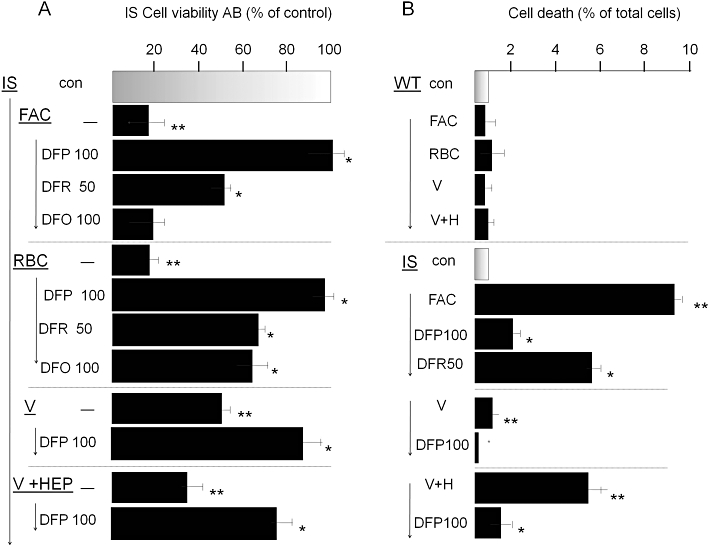
Reversal of iron toxicity in iron sensitive (IS) RAW 264.7 macrophages by chelators. IS cells were preincubated overnight with 100 µM ferric ammonium citrate (FAC), or for 1 h with opsonized erythrocytes [red blood cells (RBCs)] or 24 h with Venofer (500 µM), washed and cultured without or with added iron chelators deferiprone (DFP; 50 and 100 µM), deferasirox (DFR; 100 µM) or deferrioxamine (DFO; 100 µM). Following overnight incubation, they were assessed for cell viability with Alamar Blue (AB) (shown in A) and for maintenance of plasma membrane integrity (cell death) by the propidium iodide-Hoechst 33342 double stain described in the Methods section (shown in B). After exposure to Venofer, cells were cultured without and with hepcidin (‘V’ and ‘V + HEP’). Data are given as % of control cells (no FAC or RBC treatment) and shown as means ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. Staurosporin (0.5 µM) served as positive control and caused >90% cell death (not shown). The higher level of iron toxicity compared with that described in Figure 1 is associated with the use of lower initial cell seeding density in the cultures, necessitated by the 48 h duration of the experiment.
