Figure 3.
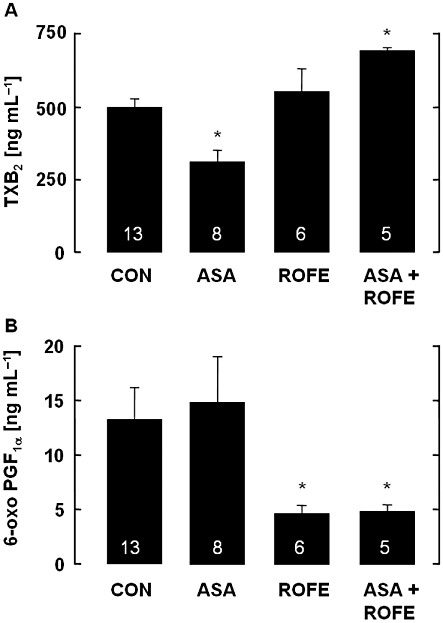
(A) Levels of TXB2 in serum of rabbits fed an atherogenic diet for 12 weeks and its modification by ASA (5 mg·kg−1 per os, bid), rofecoxib (25 mg·kg−1 per os, bid) or a combination of both. Aspirin significantly attenuated TXB2 formation, while rofecoxib had no effect. After cotreatment with ASA, rofecoxib significantly increased serum TXB2. The data are mean ± SEM of the number of experiments indicated in the columns; *P < 0.05 (ASA vs. CON and ASA + ROFE). (B) Levels of PGI2 (6-oxo PGF1α) in serum of cholesterol-fed rabbits and its modification by ASA (5 mg·kg−1 per os, bid), rofecoxib (25 mg·kg−1 per os, bid) or a combination of both. Rofecoxib significantly attenuated 6-oxo PGF1α accumulation, while ASA had no effect. Cotreatment of rofecoxib with ASA did not modify the action of rofecoxib. The data are mean ± SEM of the number of experiments indicated in the columns; *P < 0.05 (treatment vs. CON).
