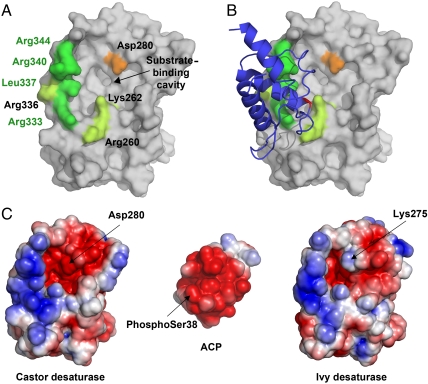
Fig. 2.
The desaturase–ACP interaction surface. (A) Surface view of the castor desaturase, looking directly at the entrance to the substrate-binding cavity. Desaturase residues that interact with ACP in the complex are colored green, with those that differ between ivy and castor and comprise the “quadruple mutant” highlighted in bright green. Asp280 is highlighted in orange. (B) The same as A, but with ACP added as a cartoon. The ACP is colored blue, with phospho-serine38 highlighted in red. (C) The electrostatic surface potentials of the desaturase–ACP interaction site. The desaturases are shown in the same orientation as A and B while ACP is rotated 180° with respect to B to show the interaction surface.