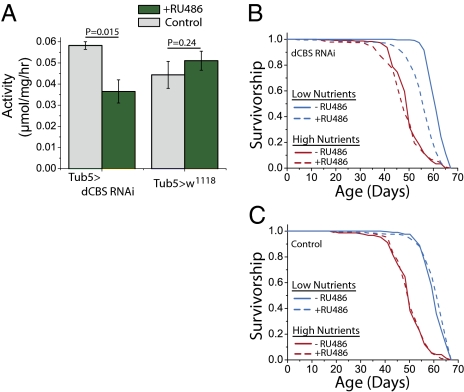
Fig. 3.
RNAi-mediated knockdown of dCBS partially reverses DR-mediated lifespan extension. (A) Transgenic expression of dCBS RNAi in diet-restricted flies by exposure to RU486 decreases CBS enzyme activity; however, there is no change in the control genotype following exposure to RU486. (B) Flies exposed to RNAi-mediated knockdown of dCBS exhibit a partial rescue of DR-mediated lifespan extension (P < 1 × 10−10). dCBS RNAi has no significant effect on lifespan in high-nutrient conditions (P = 0.22); n = 239 and n = 240 for RU486+ and RU486− (low nutrients); n = 238 and n = 240 for RU486+ and RU486− (high nutrients). (C) RU486 has no effect on lifespan in control genotypes consisting of Geneswitch tubulin (i.e., Tub5) and UAS-Dicer alone (no UAS-RNA); n = 240 and n = 240 for RU486+ and RU486− (low nutrients); n = 239 and n = 240 for RU486+ and RU486− (high nutrients).