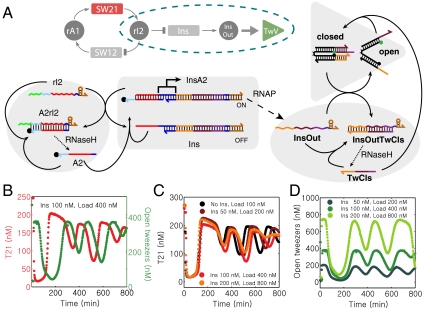
Fig. 4.
An insulator circuit (mode V coupling). (A): Insulator genelet Ins is operated in parallel with SW12. The genelet is activated by A2 and deactivated by rI2. Transcription of Ins results in RNA signal InsOut which opens tweezers previously closed by DNA strand TwCls. (“Load” for mode V is defined as closed tweezers with a 50 nM excess of TwCls, in contrast to modes I–IV where the load consists only of open tweezers.) The RNA part of hybrid duplex TwCls·InsOut is degraded by RNase H, resulting in free TwCls. This operation principle is analogous to mode I tweezers. (B): Oscillator (red) and tweezers (green) traces for 100 nM insulator genelet and 400 nM tweezers load. (C): Core-oscillator traces for 0 nM Ins and 100 nM tweezers load (black), and 200 nM (dark red), 400 nM (red), and 800 nM (orange) tweezers load and a 4∶1 ratio of tweezers:Ins. (D): Tweezers signal for 200 nM (dark green), 400 nM (green), and 800 nM (light green) tweezers load.