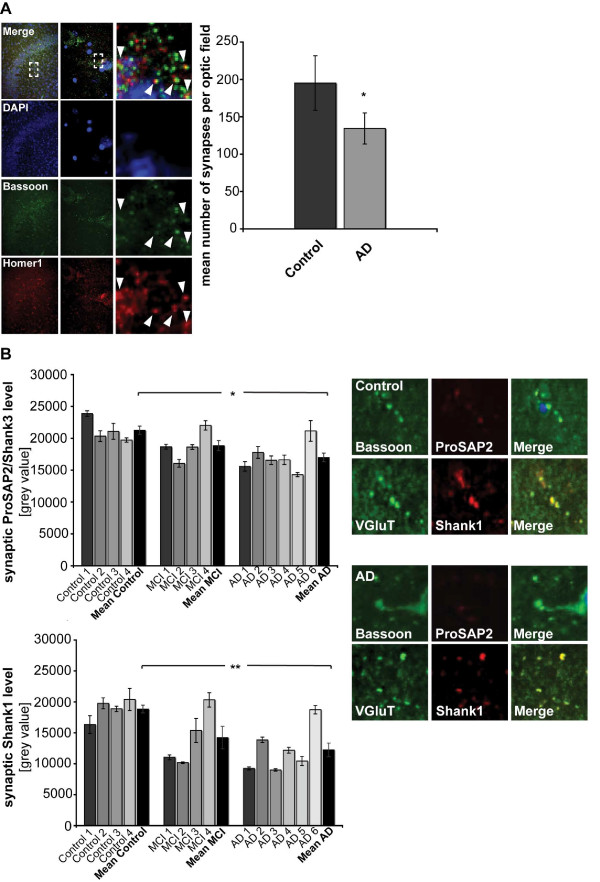
Figure 8.
Synaptic ProSAP/Shank protein levels are reduced during AD progression in hippocampal brain sections. A) Immunofluorescent images of human hippocampal brain sections (CA3), stained with DAPI and antibodies against Bassoon and Homer1 (left panel) (low, medium and high magnification images are shown to reveal Bassoon/Homer1 co-clusters). The total number of synapses (colocalizing Bassoon/Homer1 puncta) was quantified to yield the mean number of synapses per optic field in control and patients with severe Alzheimer's disease (AD) (right panel). B) Loss of synaptic ProSAP2/Shank2 and Shank1 in AD patients was assessed by quantifying the intensity of ProSAP2/Shank3 and Shank1 puncta (mean grey values) colocalizing with Bassoon or VGluT (both presynaptic marker proteins) immunopositive puncta of hippocampal sections from control, "MCI" and "AD" patients.