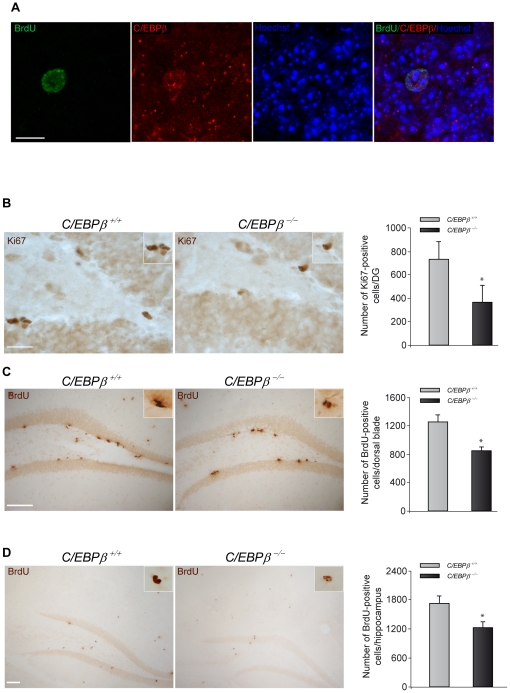
Figure 2. C/EBPβ−/− mice present less proliferation and survival of newborn cells in the hippocampus.
(A) C/EBPβ is expressed in neural stem cells of the dentate gyrus. Representative images of double-immunohistochemistry showing BrdU-positive cells (green) expressing C/EBPβ (red) in the granule layer of the hippocampus of wild type mice 28 days after BrdU injection. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst (blue). Scale bar, 10 µm. (B) Representative images showing Ki67 immunohistochemistry analysis of the DG of postnatal day 30 C/EBPβ+/+ and C/EBPβ−/− mice. Quantification of the Ki67-positive cells in the SGZ revealed that C/EBPβ−/− mice presented a significant reduction in cells positive for this proliferative marker. Scale bar, 25 µm. BrdU was administered to three month-old C/EBPβ +/+ and C/EBPβ −/− mice as explained in Materials and Methods. The animals were sacrificed one (C) or 28 days (D) after the last BrdU injection to measure proliferation or survival, respectively. BrdU immunohistochemistry and quantification analysis revealed significantly less BrdU-positive cells in the dorsal part of the dentate gyrus in C/EBPβ−/− compared to C/EBPβ+/+ mice (C). Also, the number of surviving BrdU-positive cells in the entire hippocampus was significantly reduced in C/EBPβ−/− mice (D). Scale bars, 100 µm. Insets show higher magnification. Values represent the mean ± S.E from four different animals. *P≤0.05.