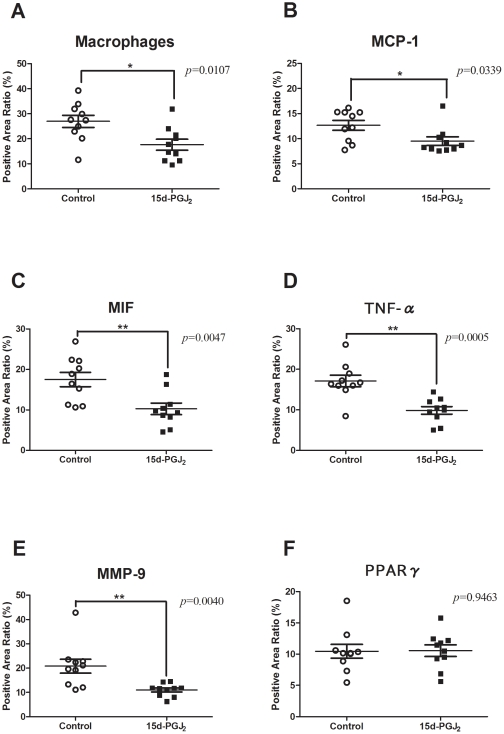
Figure 4. Prevalence of atherosclerotic lesions with immunohistochemical analysis.
Apo E-knockout mice were fed a Western-type diet and treated with PBS (control group) (n = 10) or 1 mg/kg/day 15d-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2 group) (n = 10) for 2 mo. Representative cross-sections of the aortic sinus were stained with MOMA-2, which detected macrophages, and MCP-1 Abs, MIF Abs, TNF-α Abs, MMP-9 Abs, PPARγ Abs, and counterstained with hematoxylin. We plotted the prevalence of positive areas in cross-sections of whole atherosclerotic lesions in each group. Short lines indicate the means ± SD. The prevalence of macrophage (A), immunoreactive MCP-1 (B), MIF (C), TNF-α (D) and MMP-9 (E) in atherosclerotic lesions of apo E-knockout mice treated with PBS or 15d-PGJ2 was examined. The prevalence of macrophage in the control and 15d-PGJ2 groups were 26.97±2.437% and 17.64±2.194%, respectively. The prevalence of immunoreactive MCP-1 (9.508±0.8518% vs 12.65±0.9788%, p = 0.0339), MIF (10.28±1.402% vs 17.53±1.762%, p = 0.0047), TNF-α (9.853±0.9462% vs 17.12±1.412%, p = 0.0005) and MMP-9 (11.02±0.8208% vs 20.80±2.846%, p = 0.0040) were decreased in the 15d-PGJ2 groups. But the prevalence of PPARγ (F) was not different between both groups (10.55±0.9217% vs 10.46±1.104%, p = 0.9463). *p<0.05, **p<0.01, with Student's t test.