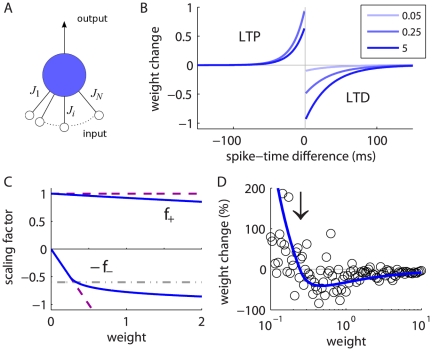
Figure 1. Single neuron equipped with STDP-plastic synapses.
A: Single neuron excited by 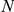 input spike trains. The synaptic strength of synapse
input spike trains. The synaptic strength of synapse  is denoted by
is denoted by 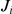 . B: Potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) curves
. B: Potentiation (LTP) and depression (LTD) curves 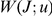 with
with 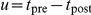 in (4). Darker curves indicate stronger values for the weight
in (4). Darker curves indicate stronger values for the weight 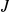 :
: 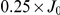 (light blue),
(light blue), 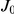 (medium blue), and
(medium blue), and 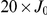 (dark blue) in (6). In the top left quadrant for LTP, the two curves in lighter blue are superimposed, since potentiation is quasi-constant for small weights. C: Functions
(dark blue) in (6). In the top left quadrant for LTP, the two curves in lighter blue are superimposed, since potentiation is quasi-constant for small weights. C: Functions 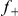 for LTP and
for LTP and 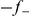 for LTD in log-STDP (blue solid curve) in (6) with
for LTD in log-STDP (blue solid curve) in (6) with 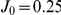 ,
, 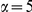 and
and 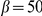 ; mlt-STDP similar to van Rossum et al.'s model [24] (pink dashed line); and add-STDP similar to Song et al.'s model [1] (gray dashed-dotted curve for depression and pink dashed curve for potentiation). D: Weight change (in percent of the original weight) resulting from 20 successive modifications induced by log-STDP with random pairing of pre- and postsynaptic spikes (within the range
; mlt-STDP similar to van Rossum et al.'s model [24] (pink dashed line); and add-STDP similar to Song et al.'s model [1] (gray dashed-dotted curve for depression and pink dashed curve for potentiation). D: Weight change (in percent of the original weight) resulting from 20 successive modifications induced by log-STDP with random pairing of pre- and postsynaptic spikes (within the range 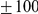 ms). In qualitative agreement with experimental measurements [19], smaller weights experience large fluctuations whereas larger weights exhibit less variability. The mean expected modification (blue solid curve) and
ms). In qualitative agreement with experimental measurements [19], smaller weights experience large fluctuations whereas larger weights exhibit less variability. The mean expected modification (blue solid curve) and 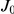 is indicated by the vertical arrow.
is indicated by the vertical arrow.