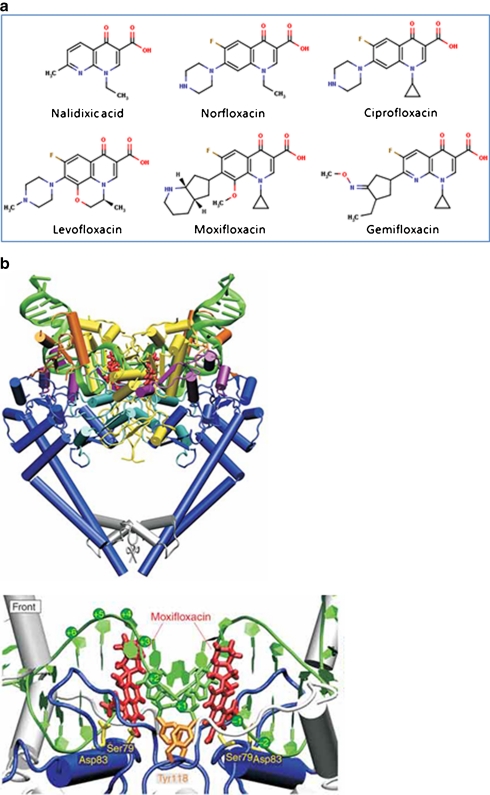
Fig. 2.
Quinolones. a Examples of fluoroquinolones and their precursor nalidixic acid. b Structure of the topo IV–fluoroquinolone complex (Laponogov et al. 2009). Upper: front view of the topo IV ParC55 and ParE30 proteins complexed with the G segment DNA and moxifloxacin, shown in cartoon representation. DNA is green, the TOPRIM domain (ParE30) is in yellow and the ParC55 is blue. The moxifloxacin molecules are shown in red. Lower: close up of the quinolone–topo IV cleavage complex in cartoon representation. The active site tyrosines (Tyr118) are in orange and the residues responsible for drug resistance upon mutation are shown in yellow (b is reproduced with permission from Nature Publishing Group; Laponogov et al. 2009)