Figure 8.
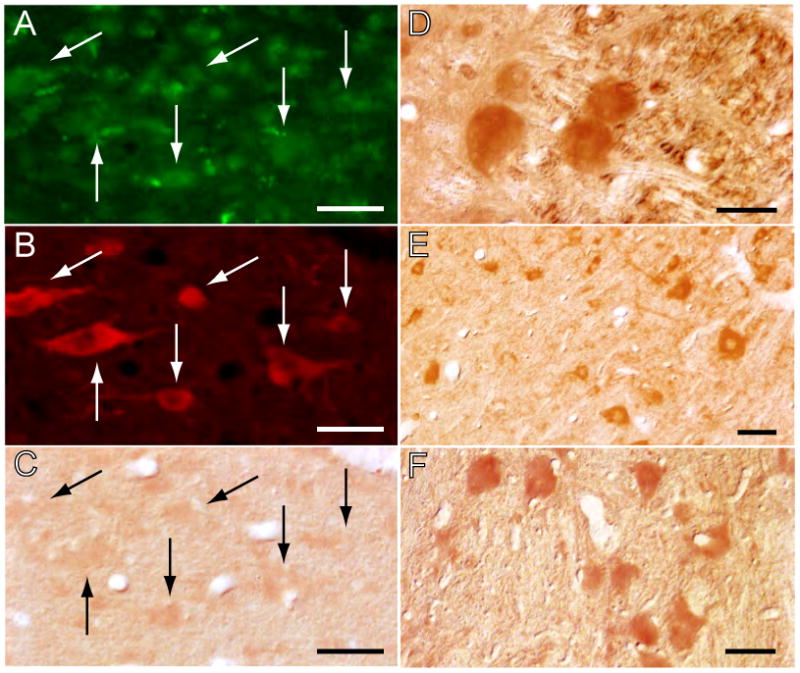
The blockade of NGF production is restricted to the site of antisense OD injections. The antisense was taken up by neurons in the LDT of a cat that was injected with an FITC-labeled control antisense into the same area where the antisense OD was applied (arrows in A); the immunolabeled neurons included a contingent of ChAT-containing cells (arrows in B). These cholinergic neurons exhibited only faint NGF immunoreactivity (arrows in C). In contrast, in nuclei more distant to the antisense OD injection, neurons were strongly immunoreactive for NGF (mesencephalic trigeminal nucleus, D; cochlear nucleus, E; and vestibular complex, F). ChAT immunolabeling was processed for rhodamine visualization; NGF immunoreactivity was visualized with the DAB method. Calibration marks, A-C, 40 μm; D, E and F, 30 μm.
