Figure 1.
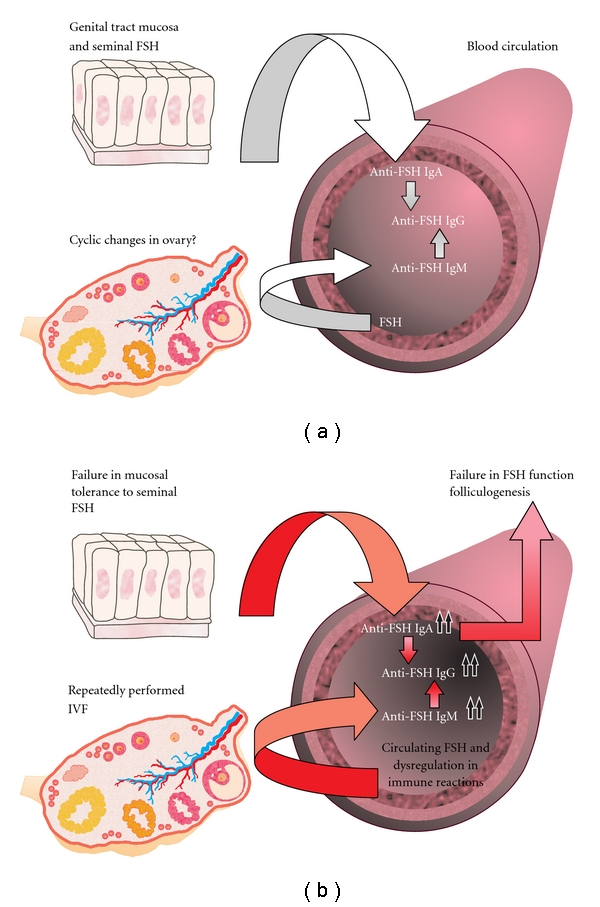
(a) Schematic overview of anti-FSH antibodies in healthy female. Antibodies detected against FSH could be natural antibodies also subjected to pregnancy-associated immune system regulations. Anti-FSH IgA detected in female circulation could be a part of the mucosal response involved in inducing immune tolerance to seminal constituents. Anti-FSH IgM associates with the peripheral level of FSH hormone and possibly contributes along with the mucosal-associated induction of IgA to the production of circulating anti-FSH IgG. (b) Increased production of naturally occurring anti-FSH antibodies in case of female infertility. The production of anti-FSH IgM and IgG antibodies could be related to a general propensity to autoimmunity or to previous IVF treatments. The elevated values of anti-FSH IgA could be explained by a genetically determined failure in mucosal tolerance in the genital tract. Anti-FSH IgG and IgA antibodies, present in sera, accumulate into the preovulatory follicle, where they affect negatively oocyte maturation.
