Fig. 3.
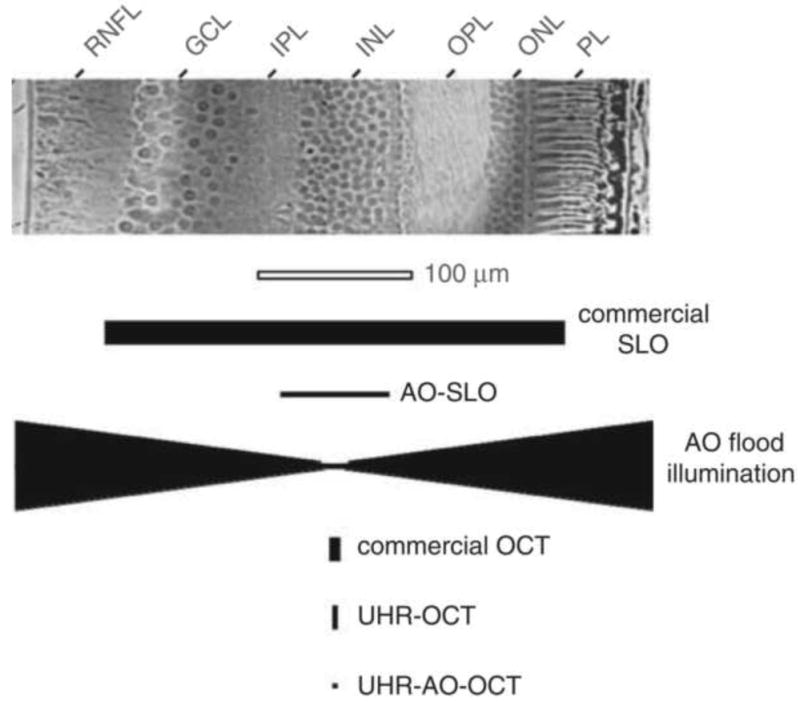
Comparison of (top) cell size in a histological cross section of the human retina with (bottom) the resolving capability of the major types of retinal imaging modalities with and without AO. The vertical and horizontal dimensions of the solid black symbols denote, respectively, the lateral and axial resolution of the instruments. Examples shown include the commercial confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope (SLO), adaptive optics confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope (AOSLO), adaptive optics flood illumination, commercial OCT, ultrahigh-resolution OCT (UHR–OCT), and ultrahigh-resolution OCT with adaptive optics (UHR–AO– OCT). GCL, ganglion cell layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PL, photoreceptor layer; RNFL, retinal nerve fiber layer. From Miller (2011).
