Fig. 6.
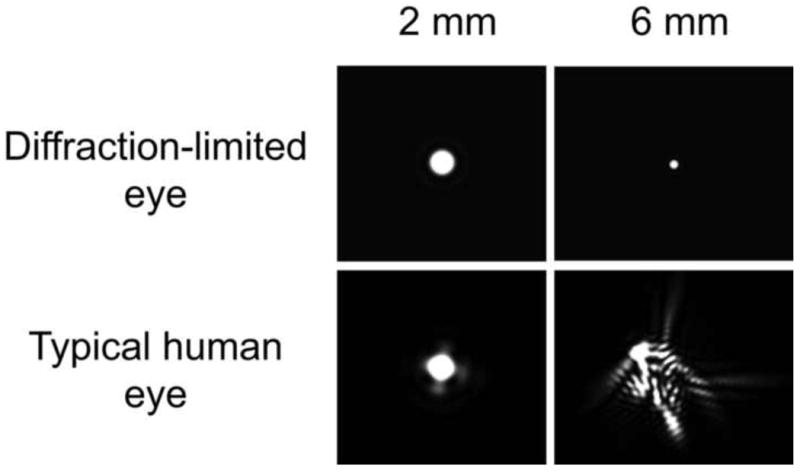
The point spread function (PSF) for a diffraction-limited eye and a normal eye at two different pupil diameters. The PSF corresponds to the light distribution on the retina produced by a point source of light infinitely distant from the eye. For the hypothetical diffraction-limited eye, the PSF diameter decreases in inverse proportion to the pupil diameter such that large pupils produce the best image quality. However, in the typical human eye, aberrations increase with increasing pupil size, eliminating the benefit of escaping diffraction at the largest pupils. The goal of AO is to correct the aberrations to produce the PSF of a diffraction-limited eye with a large pupil. (From Yin and Williams, 2010)
