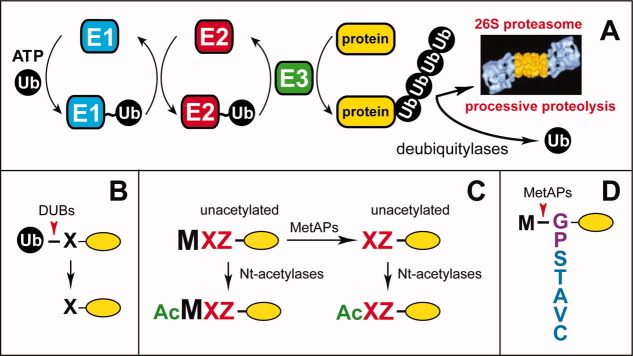
Figure 1.
The ubiquitin-proteasome system, the ubiquitin fusion technique, and N-terminal processing of newly formed proteins. A: The ubiquitin-proteasome system (Ub system).6,45–65 The conjugation of Ub to other proteins involves a preliminary ATP-dependent step in which the last residue of Ub (Gly76) is joined, via a thioester bond, to a Cys residue of the E1 (Ub-activating) enzyme. The “activated” Ub moiety is transferred to a Cys residue in one of several Ub-conjugating (E2) enzymes, and from there, through an isopeptide bond, to a Lys residue of an ultimate acceptor, denoted as “protein”. E2 enzymes function as subunits of E2-E3 Ub ligase complexes that can produce substrate-linked poly-Ub chains. Such chains have specific Ub-Ub topologies, depending on the identity of a Lys residue of Ub (which contains several lysines) that forms an isopeptide bond with C-terminal Gly76 of the adjacent Ub moiety in a chain. Specific poly-Ub chains can confer the degradation of a substrate by the 26S proteasome or other metabolic fates. Monoubiquitylation of some protein substrates can also occur, and has specific functions. One role of E3 is the recognition of a substrate's degradation signal (degron). Individual mammalian genomes encode at least a 1,000 distinct E3 Ub ligases. B: The Ub fusion technique.4,213 In eukaryotes, linear fusions of Ub to other proteins are cotranslationally cleaved by deubiquitylases at the last residue of Ub, making it possible to produce, in vivo, different residues at the N-termini of otherwise identical proteins. C: N-terminal processing of nascent proteins by Nα-terminal acetylases (Nt-acetylases) and Met-aminopeptidases (MetAPs). “Ac” denotes the Nα-terminal acetyl moiety. M, Met. X and Z, single-letter abbreviations for any amino acid residue. Yellow ovals denote the rest of a protein. D: Met-aminopeptidases (MetAPs) cleave off the N-terminal Met residue if a residue at Position 2 belongs to the set of residues shown.101 Gly and Pro at Position 2 are depicted in a different color because these residues, in contrast to other small residues, are rarely Nt-acetylated after the removal of N-terminal Met [Fig. 2(B)]. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at wileyonlinelibrary.com.]