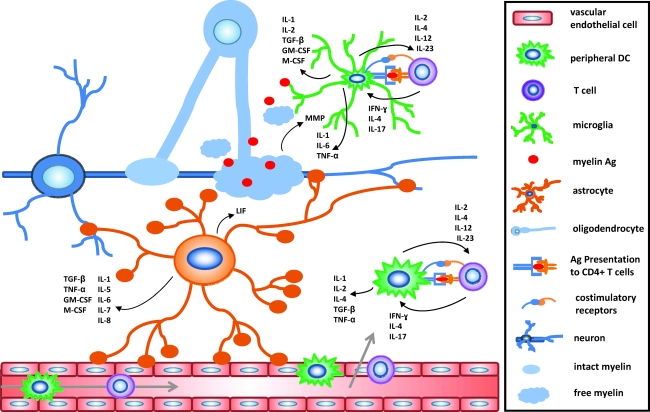
FIG. 1.
Cytokine microenvironments in the CNS during MS as a result of Ag presentation. An extensive cytokine network is created in CNS microenvironments after activation of CD4+ T cells by direct contact of the T cell receptor with MHC II on APCs as well as cell-to-cell contact between costimulatory receptor interactions present on both cell types, such as CD80/CD86. The cytokine crosstalk between autoreactive, primed T cells and APCs takes place in the CNS microenvironment and therefore can affect, and be affected by, CNS-resident cell types as well. It will be important for both potential biomarker identification and therapeutic development to determine what cell populations can act as APCs in the CNS and which cytokines are produced by a single cell at one time. CNS, central nervous system; MS, multiple sclerosis; DC, dendritic cell; APC, antigen presenting cell; Ag, antigen; IL, interleukin; IFN, interferon; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-β; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; LIF, leukemia inhibitory factor; GM-CSF, granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor.