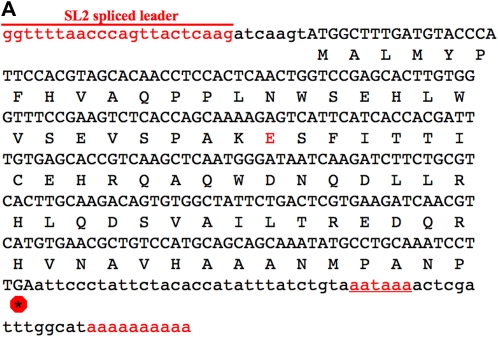
Figure 2 .
cDNA and protein sequences. (A) The emb-1 cDNA sequence from clone yk1426h04 (gift from Y. Kohara). The cDNA contains a SL2 trans-spliced leader sequence at its 5′ end and a poly(A) tail at its 3′ end, which is preceded by a polyadenylation signal (underlined), all indicated in red. Asterisk in a red octagon indicates the stop codon. Residue that is altered in the hc62ts allele is also in red (codon 30; glutamic acid). In hc62ts animals, this residue is a lysine. (B) EMB-1 is a conserved protein among Caenorhabditis species. Amino acid sequence alignment of the EMB-1 protein are from C. elegans, C. briggsae, C. remanei, and C. brenneri (www.wormbase.org). Those residues in red are identical in at least three of the four species. Indicated above the sequence is the amino acid change in residue 30. (C) Genomic region of emb-1. Shown is a schematic from www.wormbase.org of ∼5 kb of the genomic region that contains the emb-1 gene (K10D2.4). Shown in pink are the three genes that make up the operon, with emb-1 located in the middle. The deletion alleles discussed in this report (ok2759 and ok2757) are shown below as red and blue bars. The genomic fragment used for rescue is shown as a green rectangle below the operon.