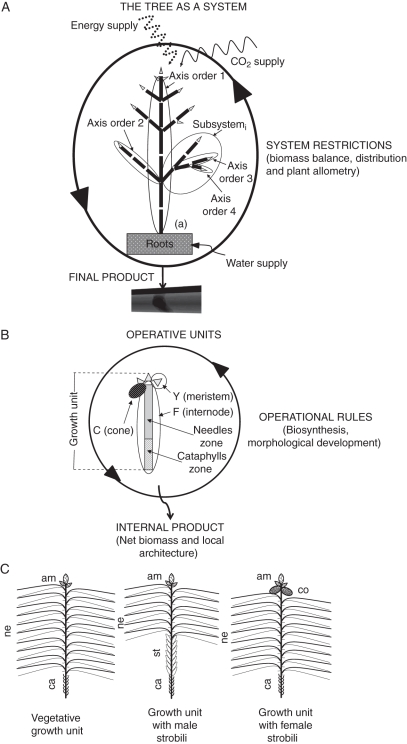
Fig. 1.
Model structure. (A) The tree is a productive system, comprising operative units organized in axes that consist of subsystems starting from a branching point. Roots are treated as a single entity. The whole system receives energy and supplies for its functioning. System restrictions such as biomass balance, distribution and plant allometry ensure a harmonic growth. (B) Operative units consist of apical meristems, internodes and cones; each operative unit obeys its operational rules and generates internal products as net biomass and local architecture. (C) P. radiata presents three types of growth units: a vegetative growth unit with cataphylls zone (ca), needles zone (ne) and lateral and terminal vegetative meristems (am); a growth unit with male strobili (st) in the zone between cataphylls (ca) and needles (ne); and a growth unit with female strobili (co) as modified branches in the lateral meristems.