Abstract
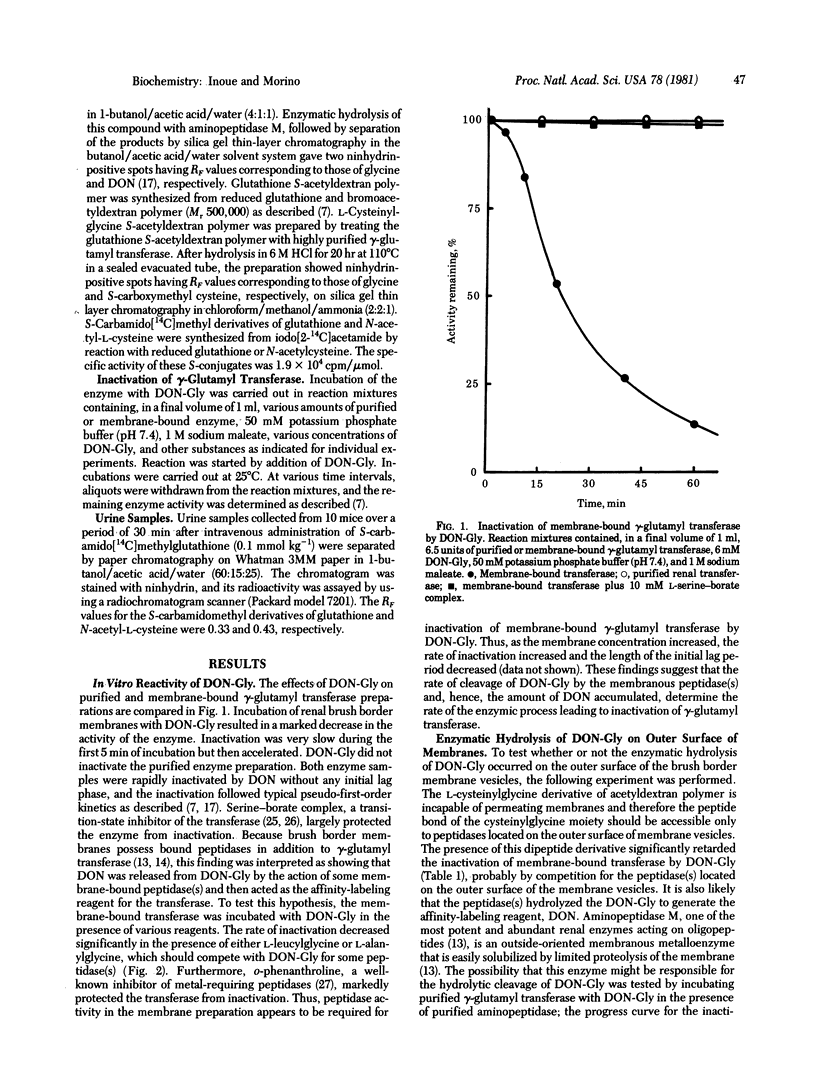
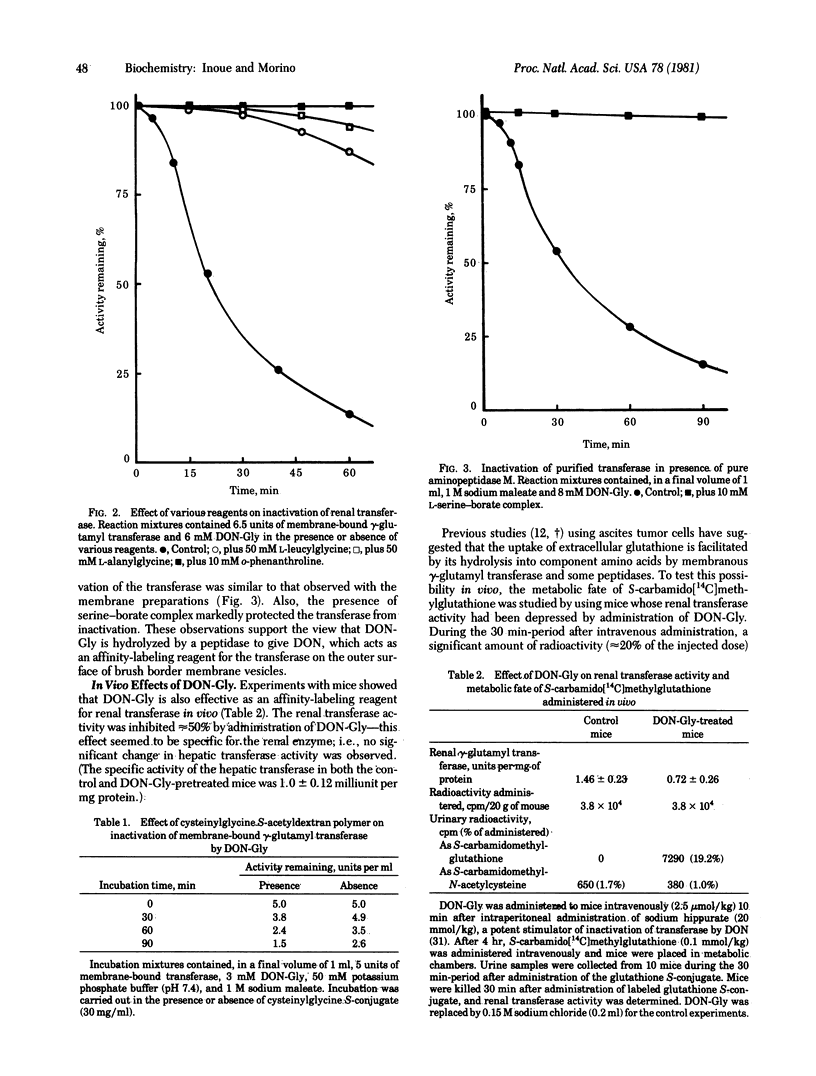
In vitro experiments showed that 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucylglycine, a dipeptide analog of L-glutaminylglycine, inactivates gamma-glutamyl transferase bound to renal brush border membrane vesicles but does not inactivate the purified transferase. The rate of inactivation of the membrane-bound enzyme decreased markedly in the presence of dipeptides, such as L-leucylglycine and L-alanylglycine, or in the presence of o-phenanthroline, an inhibitor of renal peptidases. The presence of L-cysteinylglycine S-acetyldextran polymer (Mr 500,000), which does not permeate membranes, protected the membrane-bound transferase from inactivation by 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucyglycine. This and other findings suggest that the norleucylglycine derivative was hydrolyzed by peptidase(s) bound to the outer surface of the brush border membranes and that the 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine thus released acts as an affinity-labeling reagent for the membrane-bound transferase. Similar effects were observed in vivo. Intravenous administration of 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucylglycine to mice resulted in a marked decrease in renal transferase activity. Mice thus pretreated with 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucylglycine, but not an untreated group, excreted significant amounts of S-carbamido[14C]methylglutathione in their urine within 30 min of intravenous administration of this compound. This finding suggests that the renal transferase was involved in the hydrolysis of the glutathione S-conjugate in the glomerular filtrate in vivo and that the administered 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucylglycine underwent hydrolysis peptidase(s)-catalyzed to liberate 6-diazo-5-oxo-L-norleucine that reacted with the membrane-bound gamma-glutamyl transferase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booth A. G., Kenny A. J. A rapid method for the preparation of microvilli from rabbit kidney. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;142(3):575–581. doi: 10.1042/bj1420575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan J. M. The amidotransferases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1973;39:91–183. doi: 10.1002/9780470122846.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Glutathione: interorgan translocation, turnover, and metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5606–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Meister A. Translocation of intracellular glutathione to membrane-bound gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase as a discrete step in the gamma-glutamyl cycle: glutathionuria after inhibition of transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):268–272. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTMAN S. C. THE INTERACTION OF 6-DIAZO-5-OXO-L-NORLEUCINE WITH PHOSPHORIBOSYL PYROPHOSPHATE AMIDOTRANSFERASE. J Biol Chem. 1963 Sep;238:3036–3047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper C., René A., Campbell B. J. Renal dipeptidase: localization and inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 20;242(2):446–458. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman S. C., McGrath T. F. Glutaminase A of escherichia coli. Reactions with the substrate analogue, 6-diazo-5-oxonorleucine. J Biol Chem. 1973 Dec 25;248(24):8506–8510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Inoue M., Morino Y. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: sidedness of its active site on renal brush-border membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 3;87(3):429–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. Affinity labeling of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase of tumor cell AH-130 and transport activity of glutathione and amino acids. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 21;79(4):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. Affinity labeling of rat kidney gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase by 6-diazo-5-oxo-D-norleucine. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):169–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. Affinity labeling of rat-kidney gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Mar 1;73(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11323.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue M., Horiuchi S., Morino Y. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase in rat ascites tumor cell LY-5. Lack of functional correlation of its catalytic activity with the amino acid transport. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Sep;78(2):609–615. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11774.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlenschmidt T., Curthoys N. P. Subcellular localization of rat kidney phosphate independent glutaminase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):519–524. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre T. M., Curthoys N. P. Comparison of the hydrolytic and transfer activities of rat renal gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6499–6504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A. On the enzymology of amino acid transport. Science. 1973 Apr 6;180(4081):33–39. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4081.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister A., Tate S. S. Glutathione and related gamma-glutamyl compounds: biosynthesis and utilization. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:559–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minato S. Isolation of anthglutin, an inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase from Penicillum oxalicum. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jan;192(1):235–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90088-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. GAMMA-GLUTAMYL-P-NITROANILIDE: A NEW CONVENIENT SUBSTRATE FOR DETERMINATION AND STUDY OF L- AND D-GAMMA-GLUTAMYLTRANSPEPTIDASE ACTIVITIES. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 6;73:679–681. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORLOWSKI M., MEISTER A. ISOLATION OF GAMMA-GLUTAMYL TRANSPEPTIDASE FROM HOG KIDNEY. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:338–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Meister A. The gamma-glutamyl cycle: a possible transport system for amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1248–1255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Wilk S. Synthesis of ophthalmic acid in liver and kidney in vivo. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 15;170(2):415–419. doi: 10.1042/bj1700415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus L. M. Glutamine binding sites. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:414–427. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46049-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman J. D., Goodman S. I., Mace J. W., Patrick A. D., Tietze F., Butler E. J. Glutathionuria: inborn error of metabolism due to tissue deficiency of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):68–74. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80062-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczuk A., Connell G. E. The reaction of iodoacetamide with the active center of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Aug 24;105(2):352–367. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80159-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Affinity labeling of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and location of the gamma-glutamyl binding site on the light subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Interaction of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase with amino acids, dipeptides, and derivatives and analogs of glutathione. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 10;249(23):7593–7602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tate S. S., Meister A. Serine-borate complex as a transition-state inhibitor of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4806–4809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannier C., Louvard D., Maroux S., Desnuelle P. Structural and topological homology between porcine intestinal and renal brush border aminopeptidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 11;455(1):185–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


