Abstract
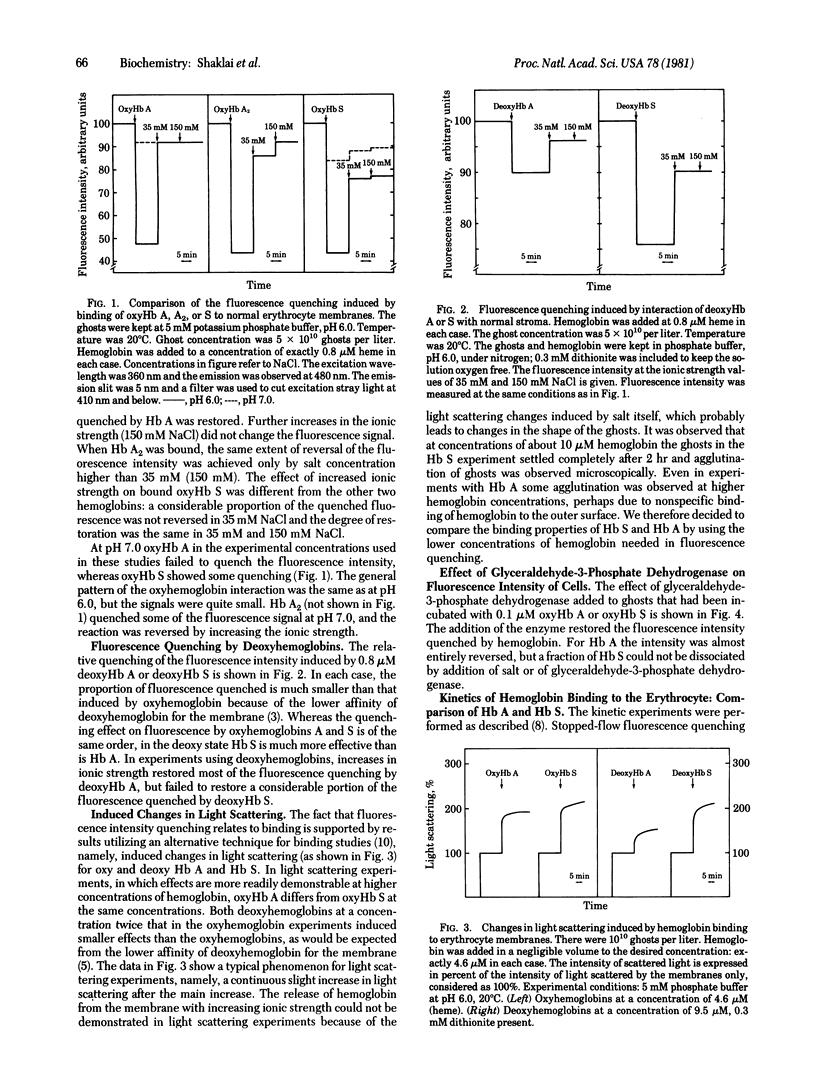
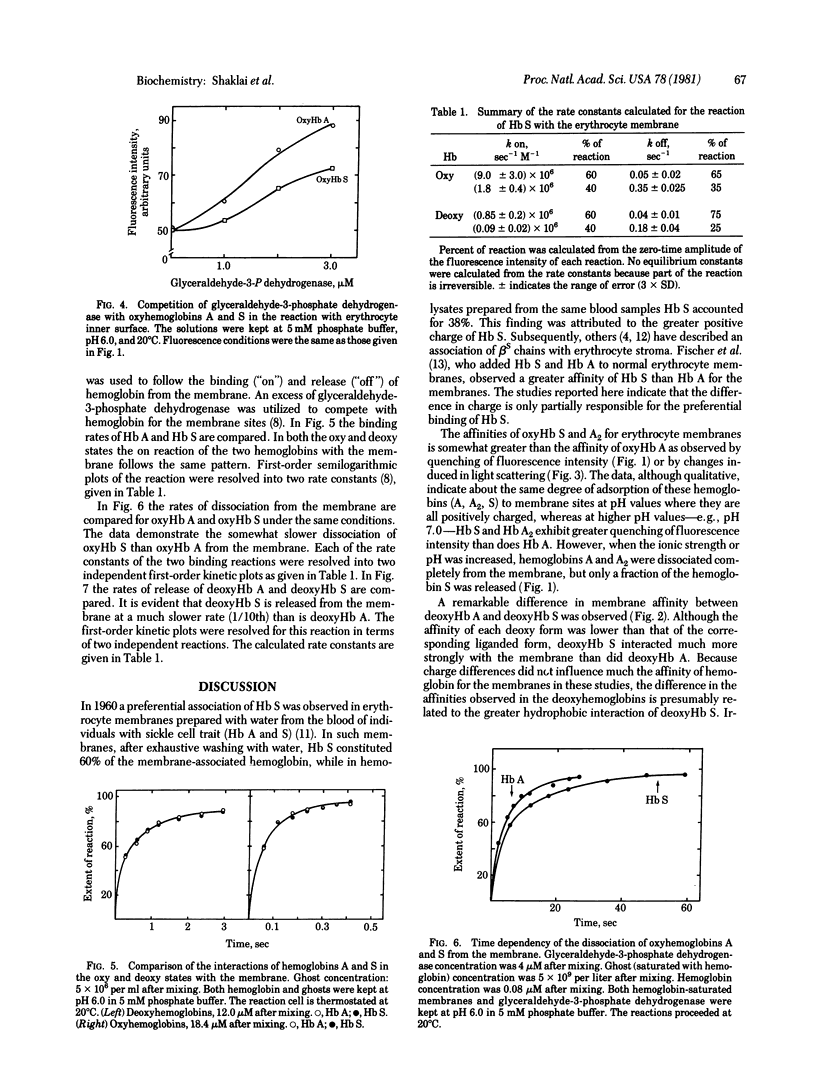
The interactions of hemoglobin S with the erythrocyte membrane were compared with the corresponding interactions of hemoglobin A by measuring in both steady-state and kinetic experiments the quenching of the fluorescence of a probe embedded in erythrocyte membranes. Whereas hemoglobin A could be dissociated from membranes, a fraction of hemoglobin S was irreversibly bound even in the oxy state. Deoxyhemoglobin S interacted much more strongly with erythrocyte membranes than did deoxyhemoglobin A: a portion of the deoxyhemoglobin S was irreversibly bound, and the reversibly bound fraction of hemoglobin S dissociated more slowly than did deoxyhemoglobin A. It is suggested that the binding of deoxyhemoglobin S is a two-step reaction in which the first step involves electrostatic interaction with band III erythrocyte membrane protein and the second step involves a hydrophobic interaction with membrane lipids. The latter reaction reflects the greater hydrophobicity of hemoglobin S. The unique interaction of hemoglobin S with erythrocyte membranes may be important in the formation of irreversibly sickled cells.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bank A., Mears G., Weiss R., O'Donnell J. V., Natta C. Preferential binding of beta s globin chains associated with stroma in sickle cell disorders. J Clin Invest. 1974 Oct;54(4):805–809. doi: 10.1172/JCI107820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calissano P., Alemà S., Rusca G. Effect of haemoglobin on liposome permeability to Rb + and other solutes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 17;255(3):1009–1013. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton J. W., Berger E., White J. G., Jacob H. S. Calcium-induced damage of haemoglobin SS and normal erythrocytes. Br J Haematol. 1978 Jan;38(1):57–62. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1978.tb07108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Nagel R. L., Bookchin R. M., Roth E. F., Jr, Tellez-Nagel I. The binding of hemoglobin to membranes of normal and sickle erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Feb 14;375(3):422–433. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90357-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glader B. E., Nathan D. G. Cation permeability alterations during sickling: relationship to cation composition and cellular hydration of irreversibly sickled cells. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):983–989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Yamada O., Moldow C. F., Jacob H. S., White J. G., Eaton J. W. Abnormal adherence of sickle erythrocytes to cultured vascular endothelium: possible mechanism for microvascular occlusion in sickle cell disease. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jan;65(1):154–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI109646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen W. N., Lessin L. S. Membrane alterations associated with hemoglobinopathies. Semin Hematol. 1970 Oct;7(4):409–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIPSTEIN F. A., RANNEY H. M. Electrophoretic components of the hemoglobin of red cell membranes. J Clin Invest. 1960 Dec;39:1894–1899. doi: 10.1172/JCI104213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Phospholipid-protein interactions: membrane permeability correlated with monolayer "penetration". Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):805–809. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessin L. S., Kurantsin-Mills J., Wallas C., Weems H. Membrane alterations in irreversibly sickled cells: hemoglobin--membrane interaction. J Supramol Struct. 1978;9(4):537–554. doi: 10.1002/jss.400090408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERUTZ R. R., LIQUORI A. M., EIRICH F. X-ray and solubility studies of the haemoglobin of sickle-cell anaemia patients. Nature. 1951 Jun 9;167(4258):929–931. doi: 10.1038/167929a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany J. M., Shaklai N. Functional properties of human hemoglobin bound to the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1979 Mar 6;18(5):893–899. doi: 10.1021/bi00572a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. G., Takeda I., Gustavson L. P., Alperin J. B. Intraerythrocytic precipitations of haemoglobins S and C. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 19;235(55):88–90. doi: 10.1038/newbio235088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklai N., Abrahami H. The interaction of deoxyhemoglobin with the red cell membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1105–1112. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91586-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklai N., Sharma V. S. Kinetic study of the interaction of oxy- and deoxyhemoglobins with the erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklai N., Yguerabide J., Ranney H. M. Classification and localization of hemoglobin binding sites on the red blood cell membrane. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5593–5597. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaklai N., Yguerabide J., Ranney H. M. Interaction of hemoglobin with red blood cell membranes as shown by a fluorescent chromophore. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5585–5592. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata K., Cottam G. L., Waterman M. R. Acceleration of the rate of deoxyhemoglobin S polymerization by the erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jan 28;110(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


