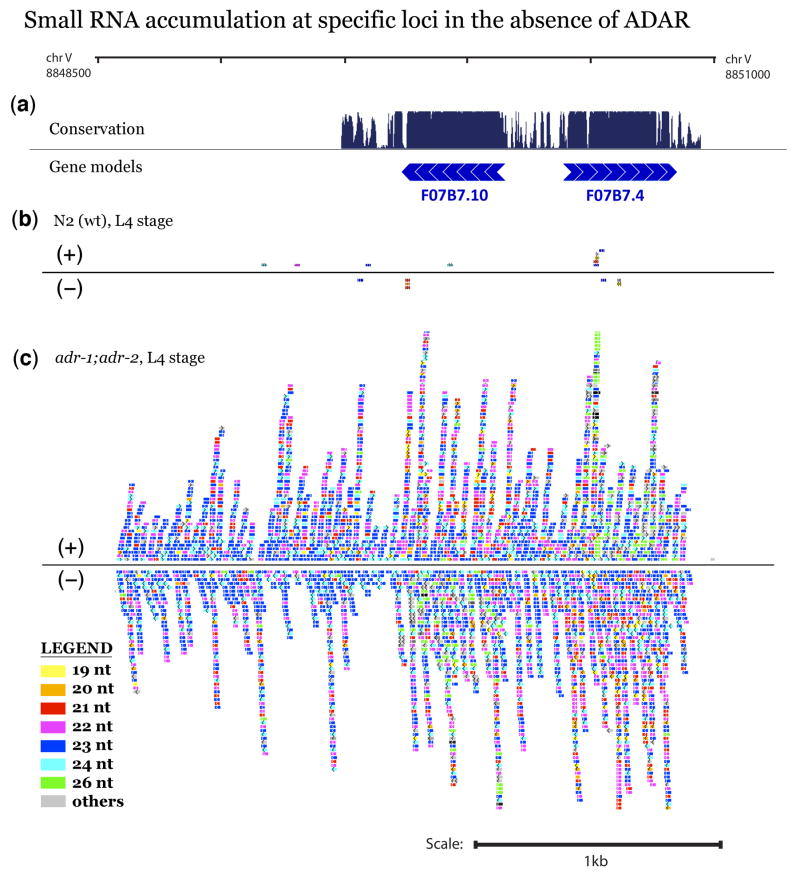
Figure 2. Small RNA accumulation at the F07B7 histone locus in the absence of ADAR activity.
An exemplary region spanning 2.6 kb (overlapping the F07B7.10 and F07B7.4 regions of C. elegans chromosome V) is shown. (a) Identified coding regions and conservation are diagrammed as UCSC Genome Browser tracks (C. elegans genome version WS190)59. F07B7.10 encodes an H2A histone; F07B7.4 encodes an H2B histone. Direction of transcription is depicted by arrows. (b–c) Small RNAs mapping to this region from (b) N2 and (c) adr-1;adr-2 animals. Each colored rectangle represents up to 10 instances of a distinct small RNA sequence per five million sequenced sRNAs. Small RNAs aligning to the (+) strand are drawn above the line and those aligning to the (−) strand are drawn below the line. Overall numbers of aligned reads for the wild type and adr mutant datasets in this example were 9.2 million and 10.1 million, respectively, (Supplementary Table 1) with comparable representation of miRNAs, 21-U RNAs, and endo siRNAs in the two samples. Additional examples of small RNA coverage are shown in Supplementary Figure 4. Colors indicate sizes (as on figure legend): yellow=19 nt, orange=20 nt, red=21 nt, magenta=22 nt, blue=23 nt, cyan=24 nt, green=26 nt, grey=all other lengths.