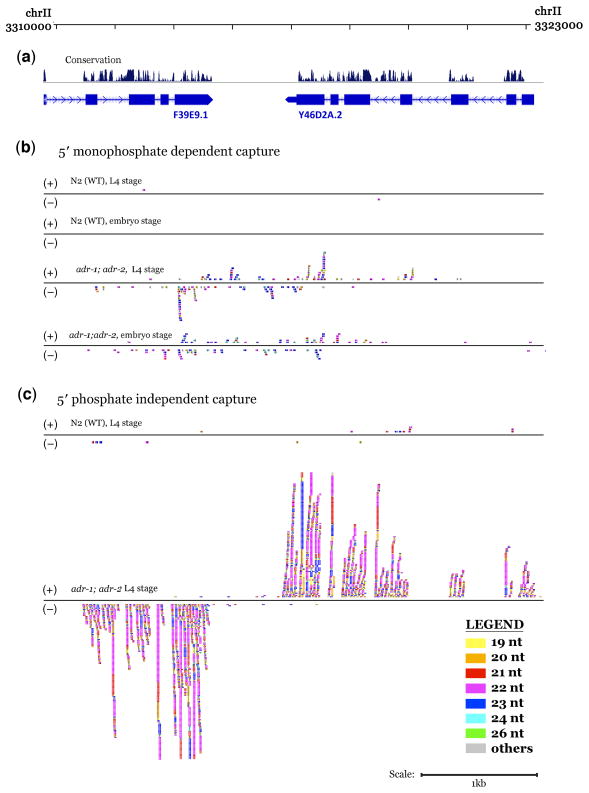
Figure 5.
A substantial class of additional ARL-associated siRNAs are evident in 5′ phosphate independent capture and sequencing. (a) UCSC Genome Browser map (C. elegans genome version WS190) displaying an ARL in the intergenic region between genes F39E9.1 (split into F39E9.1 and F39E9.22 in WS215) and Y46D2A.2 (split into Y46D2A.2 and Y46D2A.5 in WS215), overlapping the last exon of both genes. Direction of transcription is depicted by arrows. (b) Populations of 5′ phosphorylated small RNAs. A substantial increase in small RNA accumulation in adr-1;adr-2 animals over wild-type levels can be seen at both the embryo and L4 stages. (c) Populations of small RNAs that have been exposed at the 5′ end by sequential treatment with alkaline phosphatase followed by polynucleotide kinase. Small RNAs accumulate (with size preference for 21–22 nt and a distinct strand preference) in adr-1;adr-2 animals over wild-type levels at both transcribed loci overlapping the ARL.