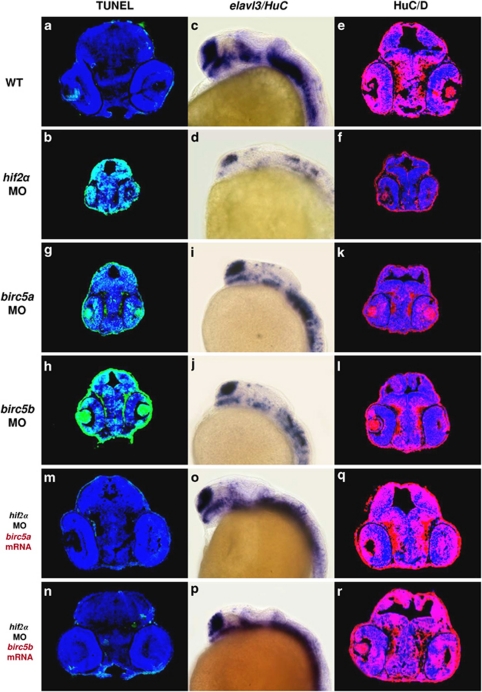
Figure 6.
Survivin orthologues function downstream of HIF2α to control CNS development. (a and b) Transverse brain sections with TUNEL staining in 48 h.p.f. wild-type (WT; a) and hif2α ATG-MO (b) embryos. (c and d) Lateral views of elavl3 expression in WT (c) and hif2α ATG-MO (d) 24 h.p.f. embryos. (e and f) Immunofluorescent staining of HuC/HuD (in red) in transverse brain sections of WT (e) and hif2α ATG-MO (f) 48 h.p.f. embryos. Nuclei are labeled by DAPI staining (in blue). (g and h) Transverse brain sections with TUNEL staining in birc5a ATG-MO (g) and birc5b ATG-MO (h) 48 h.p.f. embryos. Knockdown of birc5a and birc5b induced CNS apoptosis. (i and j) Lateral views of elavl3 expression in birc5a ATG-MO (i) and birc5b ATG-MO (j) 24 h.p.f. embryos. Compared with WT, birc5a and birc5b MO embryos exhibited lower elavl3 expression, and a similar pattern was found in hif2α MO embryos. (k and l) Immunofluorescent staining of HuC/HuD in transverse brain sections of birc5a ATG-MO (k) and birc5b ATG-MO (l) 48 h.p.f. embryos. The loss of neural differentiation in birc5a and birc5b MO embryos was confirmed by the deficiency in post-mitotic HuC/D expression. (m and n) Transverse brain sections with TUNEL staining in 48 h.p.f. hif2α ATG-MO embryos injected with 50 pg of birc5a mRNA (m) or birc5b mRNA (n). The intensive apoptosis observed in the hif2α morphants was effectively eliminated by either ectopic addition of birc5a or birc5b mRNA. (o and p), Lateral views of elavl3 expression in 24 h.p.f. hif2α ATG-MO embryos injected with 50 pg of birc5a mRNA (o) and birc5b mRNA (p). (q and r) Immunofluorescent staining of HuC/HuD in transverse brain sections of 48 h.p.f. hif2α ATG-MO embryos injected with 50 pg of birc5a mRNA (q) and birc5b mRNA (r). The loss of elavl3 expression in hif2α morphants was rescued by in vitro transcribed birc5a or birc5b mRNA