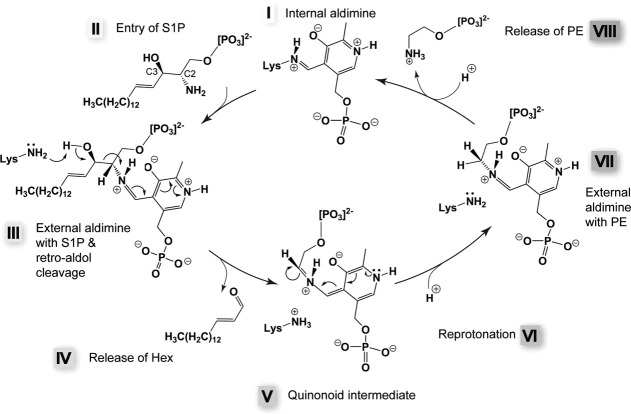
Figure 5.
Proposed SPL reaction mechanism.82 In the resting state, a lysine (311 in StSPL) forms a Schiff base with the aldehyde group of PLP (step I). The incoming substrate (S1P in the scheme, step II) triggers transaldimination and replaces the lysine as Schiff base partner of PLP. The resulting S1P-PLP complex is called external aldimine [step III, model presented in Figure 4(B), colored green]. After retro-aldol cleavage (step III), the long-chain aldehyde product (Hex in the scheme) leaves the active site (step IV) and a quinonoid intermediate is formed (step V). A stereospecific reprotonation (step VI) of this intermediate yields the second external aldimine (step VII). We propose that one of the two conserved lysines strictly required for activity carries out the retro-aldol cleavage in step III as well as the reprotonation (step VI). PE is then released (step VIII) and the internal aldimine is re-formed (step I).