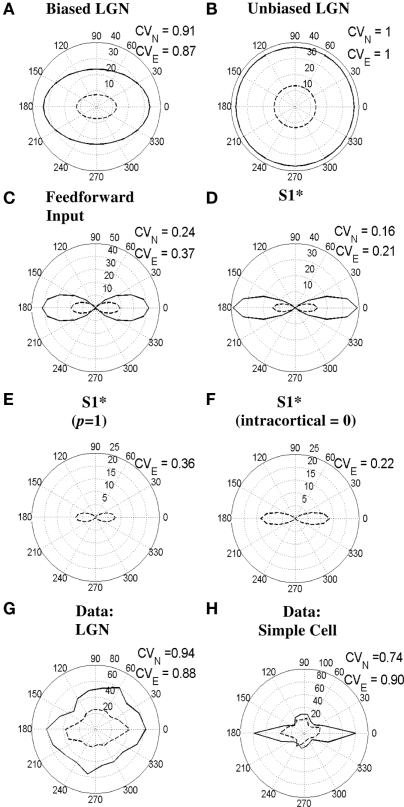
Figure 11.
Effects of electrical stimulation in the LGN on orientation selectivity of LGN and simple cells. (A–F) show simulations for the simple cell S1* (see text) in response to bars of length 4.17° either without or during electrical stimulation of the LGN. (A,B) show the responses of the orientation-biased and unoriented LGN cells that provide the feed-forward input to the simple cell, respectively. (C,D) show the responses of the combined feed-forward input to, and the output of, the S1* simple cell, respectively. (E,F) illustrate the output of the S1* simple cell when either the power-law exponent is reduced to p = 1 (from 1.85) or the intra-cortical input is set to zero (i.e., Wce = Wci = Wse = Wsi = 0), respectively. (G,H) demonstrate the responses of a real LGN cell and a real simple cell to bars, respectively, both with or without electrical stimulation in the LGN (adapted from Viswanathan et al., 2011). In all subfigures, responses to visual stimulation alone are indicated by the solid lines, whereas responses to visual stimulation during electrical stimulation are indicated by the dashed lines. Moreover, the CVN and CVE values next to each subfigure indicate the circular variance values calculated from the responses to normal visual stimulation alone or visual stimulation during electrical stimulation, respectively.