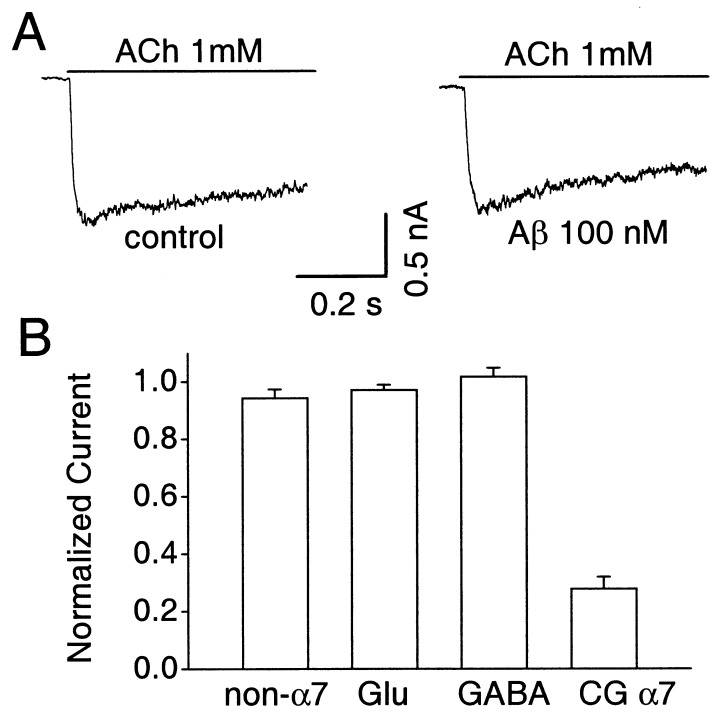
Figure 2.
Effects of 100 nM Aβ1–42 on other ionotropic receptors. Cells were voltage-clamped at −60 mV. (A) Representative example showing the slowly desensitizing, αBgt-resistant ACh responses of a neuron with non-α7-nAChRs before (Left) and during (Right) application of Aβ1–42. (B) Compiled data showing the absence of significant Aβ1–42 blockade on peak responses from non-α7-nAChRs (non-α7), glutamate receptors (Glu), and GABAA receptors (GABA) on rat hippocampal neurons and the presence of blockade for α7-nAChRs on chick ciliary ganglion neurons (CGα7). Mean initial responses (in nanoamperes) from Left to Right were 0.8 ± 0.2 (n = 6), 3.2 ± 0.7 (7), 4.3 ± 1.2 (4), and 4.5 ± 0.5 (8).