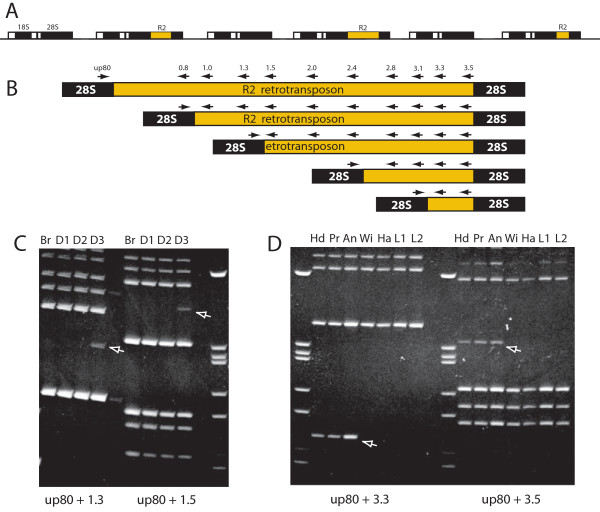
Figure 1.
Diagram of R2 insertions within the rRNA genes of Drosophila and the PCR assay used to monitor somatic mosaicism. (A) Diagram of the tandemly repeated rRNA genes of Drosophila simulans and the location of R2 insertions. Black boxes, 18S, 5.8S and 28s rRNA genes (5.8S gene between the 18S and 28S genes is not labeled); white boxes, transcribed spacer regions. (B) About half of the R2 insertions have deletions of their 5' end that can extend to nearly the entire length of the element. All R2 copies have the same 3' junction with the 28S gene. Arrows above the R2/28S diagrams indicate the positions of the oligonucleotide primers used to assay for the 5' truncations. The DNA extraction method, the primers used and the PCR protocols used were identical to those in previous reports [11-13]. (C) Examples of the ethidium stained PCR products derived from larval tissues. The larval tissues were dissected in Drosophila Ringers. (D) Examples of the ethidium stained PCR products derived from adult tissues. Adult tissues were placed directly in the DNA extraction solution. PCR bands interpreted as somatic insertions are indicated with arrows. To be scored as a somatic mosaic the amplified band had to be detected with two sets of primer combinations (shown below the figures). The following abbreviations for body segments were used: An = antenna; Br, brain from a larvae; D1-D3, individual pairs of imaginal disc (the specific disc pair used was not known); Ha = haltere; Hd = head; L1 and L2 = individuals legs from different body segments; Pr = proboscis; Wi = wing.