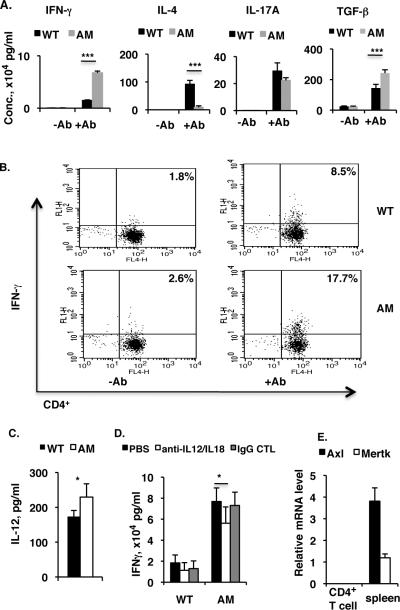
Figure 1. In vitro activation of CD4+ T cells by plate-bound anti-CD3 antibody and soluble anti-CD28 antibody induces more INF-γ-secreting Th1 cells in AM dko mice than in the wild-type.
A, Pooled spleen and lymph node CD4+ T cells were isolated from WT or AM dko mice by a initial Nylon-wool column filtration and followed by EasySepTM mouse CD4 positive selection kit (StemCell Technologies). 8×105 CD4+ T cells per well were plated on a 96-well plate bound with anti-CD3 (5 μg ml−1) in the presence of soluble anti-CD28 (1 μg ml−1) antibody. The control cells were plated on a 96-well plate in the absence of bothanti-CD3 and -CD28 antibodies. After two days of culture, levels of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-17A, and TGF-β in the culture medium were measured by Ready-Set-Go ELISA kits following manufacturer's instruction (eBioscience). B, Pooled naïve spleen and lymph node CD4+ T cells from wild-type or dko mice were cultured in 96-well plates as in (A), then IFN-γ-secreting CD4+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry on a 4-color BD-FACSCalibur (BD Biosciences). The result is one representative of three mice in each group. C, The cell culture media prepared from (A) was subjected to IL-12 measurement by Ready-Set-Go ELISA kit (eBioscience). The concentration of IL-12 is expressed as pg/ml. D, 8×105 CD4+ T cells prepared as described in (A) were plated on a 96-well plate and stimulated for 48 h by plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 antibodies, in the presence of neutralizing antibodies against IL-12 (2 μg/ml, C17.8, eBiosciences) and IL-18 (2 μg/ml, 93–10C, MBL-International Corp); and the controls use either PBS or rat IgG1-κ isotype monoclonal antibody (2 μg/ml, eBRG1, eBiosciences) in the place of neutralizing antibodies. The culture medium after 48 h was subjected to IFN-γ measurement as in (A), and the concentration of IFN-γ is expressed as ×104 pg/ml. E. No expression of Axl and Mertk in the naïve WT CD4+ T cells. Pooled WT spleen and lymph node CD4+ T cells were first enriched by a initial Nylon-wool column filtration and then purified on a high-speed cell sorter (MoFlo, Dako Cytomatino, Fort Collins, CO), and 1×106 CD4+ T cells with purity >98% were subjected to RNA isolation and 1 μg of total RNA was used for reverse transcription and real-time qPCR analysis of Axl and Mertk expression. The total RNA from WT control spleens was used as positive control. The results in (A, C and D) are the mean ±SD for 5 wells per group in one experiment and are representative of those obtained in three independent experiments *p<5, ***p<0.001 in the one-way ANOVA test using ProStat Ver 5.5.