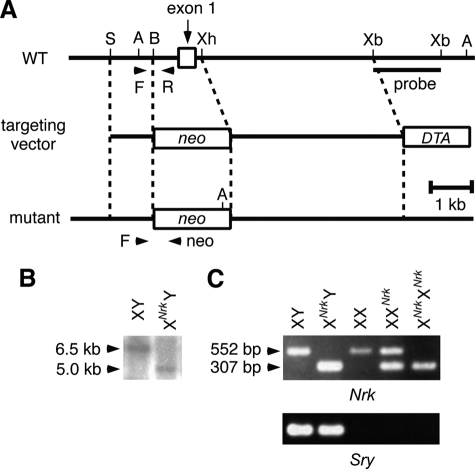
FIGURE 1.
Generation of Nrk-null mice. A, schematic structure of the Nrk targeting vector, as well as of the WT and Nrk-null alleles. Arrowheads (F, R, and neo) indicate the positions of PCR primers used for genotyping in C. DTA, diphtheria toxin A gene; neo, neo-resistance gene; A, AccI; B, BamHI; S, SpeI; Xb, XbaI; Xh, XhoI. The position of the probe used for Southern blotting in B is also indicated. B, genomic DNAs from WT and XNrkY mouse ES cells were digested with AccI and examined by Southern blotting using the XbaI-XbaI fragment within intron 1 as a probe. The WT and mutant alleles yielded 6.5- and 5.0-kb fragments, respectively. C, PCR genotyping using tail DNAs from XY, XNrkY, XX, XXNrk, and XNrkXNrk mice as templates (top). This PCR amplified 552- and 307-bp fragments from the WT and mutant alleles, respectively. The sex of mice was confirmed by PCR of the Sry gene in the male-specific Y chromosome (bottom).