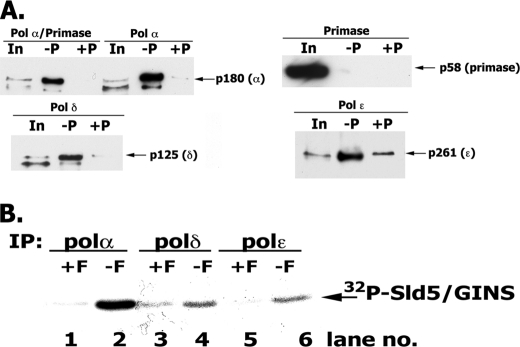
FIGURE 6.
Interaction of hGINS with replication Pols. A, interaction of GINS and Pols detected following infection of High Five insect cells. High Five insect cells were infected with viruses expressing the indicated FLAG-tagged Pols and the four GINS subunits (including GST-Sld5). After infection, cells were lysed, and the GST-GINS (and associated proteins) was pulled-down with glutathione-agarose beads as described under “Experimental Procedures.” GST-precipitated material was subjected to 4–20% polyacrylamide gradient gel/SDS electrophoresis and Western blotting, and bands were visualized with Pol-specific antibodies. In, 1% of input; −P, GST pull-down carried out without Precission protease treatment; +P, GST pull-downs carried out following Precission protease treatment. B, in vitro interaction of GINS and Pols. Reaction mixtures (100 μl) containing 3 pmol of FLAG-tagged Pol α-primase complex (or Pol δ or Pol ϵ) and 5 pmol of 32P-labeled GINS (1454 cpm/fmol) were incubated in Binding Buffer (50 mm HEPES, pH 7.5, 0.05% Nonidet P-40, 100 mm NaCl, 0.1 mg/ml BSA, and protease inhibitors) for 16 h at 4 °C. After incubation, reaction mixtures were divided into two equal aliquots, 15 μl of FLAG-agarose beads were added to both, and FLAG peptide (final concentration, 1 mg/ml) was added to one aliquot (+F) that served as a negative control. Pols were immunoprecipitated (IP) with FLAG antibody for 2 h at 4 °C, and the beads were washed three times with 0.5 ml of Binding Buffer. The bound proteins were eluted by boiling the beads in 15 μl of 1× SDS loading buffer, and the proteins were resolved in 12% SDS-PAGE; GINS was detected by autoradiography and phosphorimaging.