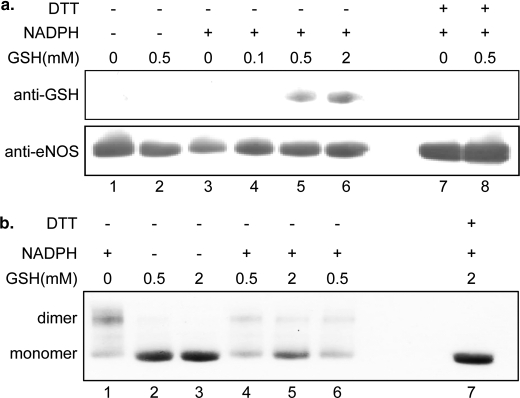
FIGURE 4.
Mechanistic study of eNOS S-glutathionylation and interdisulfide bond formation. a, O2˙̄ generated from BH4-free eNOS induces protein S-glutathionylation formation. The upper panel is eNOS S-glutathionylation formation through eNOS protein thiyl radical in the presence of GSH, when eNOS is uncoupled, and immunoblotting against anti-GSH antibody. Lane 1 is eNOS only. Lane 2 is eNOS with 0.5 mm GSH. Lane 3 is the uncoupled eNOS. Lane 4 is the uncoupled eNOS with 0.1 mm GSH (20 min). Lane 5 is the uncoupled eNOS with 0.5 mm GSH (20 min). Lane 6 is the uncoupled eNOS with 2 mm GSH (20 min). Lanes 7 and 8 are samples from lanes 3 and 5, respectively, treated with 1 mm DTT. The lower panel shows immunoblotting for eNOS. b, O2˙̄ generated from BH4-free eNOS induces eNOS interdisulfide formation. Immunoblotting against anti-eNOS antibody is used to determine eNOS monomer and dimer under the nonreducing SDS-PAGE separation. Lane 1 is the uncoupled eNOS. Lanes 2 and 3 are eNOS with 0.5 or 2 mm GSH, respectively. Lane 4 is the uncoupled eNOS with 0.5 mm GSH (20 min). Lane 5 is the uncoupled eNOS with 2 mm GSH (20 min). Lane 6 is the uncoupled eNOS with 0.5 mm (60 min). Lane 7 is sample from lane 5 treated with 1 mm DTT.