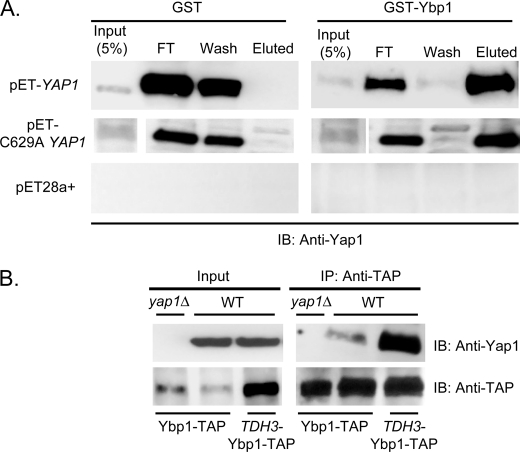
FIGURE 6.
Yap1 and Ybp1 interact in vitro and in vivo. A, recombinant forms of Yap1 (pET-YAP1) and Ybp1 (GST-Ybp1) were prepared in Escherichia coli and purified by standard techniques. Glutathione S-transferase (GST) or GST-Ybp1 were bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads. Next, protein lysates from cells containing an empty expression vector (pET28a+) or the same vector driving bacterial expression of Yap1 (pET-YAP1) or a constitutively nuclear mutant form (C629A YAP1) were applied. An aliquot of the lysate (Input) was blotted to estimate binding efficiency. After binding, unbound material was collected (FT) and the beads were washed with buffer (wash). Finally, bound material was eluted with reduced glutathione (Eluted). Samples of each fraction were resolved on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting with the anti-Yap1 antibody. B, isogenic wild-type or yap1Δ cells containing the indicated YBP1-TAP fusion genes were grown to mid-log phase and protein extracts were prepared. Equal aliquots of these extracts (Input) were retained to permit confirmation of the presence of each protein. Ybp1-TAP was immunoprecipitated using the anti-TAP antibody. These immunoprecipates (IP), together with the input samples, were resolved on SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting (IB) using the indicated antibodies.