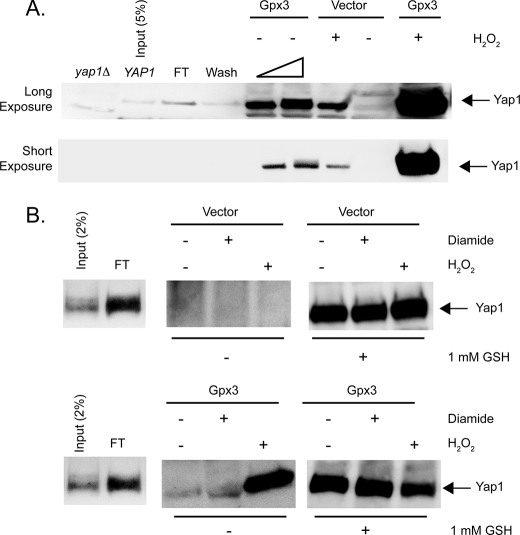
FIGURE 7.
Yap1 can be released from complex formation with Ybp1 by addition of Gpx3 and H2O2. A, a bacterial lysate expressing glutathione S-transferase-Ybp1 was bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads. After washing, these beads were incubated with a protein extract prepared from cells containing a pET28a+ plasmid producing Yap1. This extract was mixed with the GSH-Sepharose bound GST-Ybp1 to form an immobilized GST·Ybp1·Yap1 complex bound to Sepharose-GSH. The beads containing the GST·Ybp1·Yap1 complex were then treated with protein lysates from bacterial cells expressing Gpx3 or containing the empty pET28b+ vector plasmid only. Where indicated, 1 mm H2O2 was added to the extracts and incubated for 10 min at room temperature. The eluate from each column was collected and concentrated by precipitation with TCA. The precipitates were washed with acetone, resuspended in 1× Laemmli buffer, and electrophoresed through SDS-PAGE. After transfer to nitrocellulose membranes, the presence of Yap1 was assessed by Western blotting using the rabbit anti-Yap1 antiserum. Protein extracts from yeast cells lacking the Yap1 protein (yap1Δ) and bacterial lysate from cells expressing Yap1 (YAP1) were analyzed as controls for the location of authentic Yap1 in this assay. A sample of the Yap1-containing extract corresponding to 5% of the total was analyzed here. FT indicates the amount of recombinant Yap1 that failed to associate with the GSH-Sepharose bound GST-Ybp1. Wash denotes the amount of Yap1 that was eluted from the column by low-salt buffer treatment. The bar of increasing width refers to the use of 20 or 40 μg of extract from Gpx3-expressing cells in these two lanes. 40 μg of extract was used in all other lanes. The top panel presents a long exposure of the same Western blot to increase the ability to detect Yap1, whereas the lower panel is a short exposure that emphasizes the dramatic increase in Yap1 release in the presence of Gpx3 and H2O2. B, beads containing GST·Ybp1·Yap1 complexes were formed as above. These beads were then incubated with protein extracts from cells containing the empty expression vector pET28b+ (Vector) (top panel) or the same plasmid expressing Gpx3 (Gpx3) (bottom panel). These incubations were carried out with no additions or with the addition of 1 mm diamide or H2O2 as indicated. Eluates were collected and blotted for the presence of Yap1 as above. After elution, the beads were then treated with 1 mm reduced GSH to elute the remaining Yap1. These GSH-dependent eluates were also concentrated by TCA precipitation and subjected to Western blot analysis to determine the level of Yap1 remaining on the column.