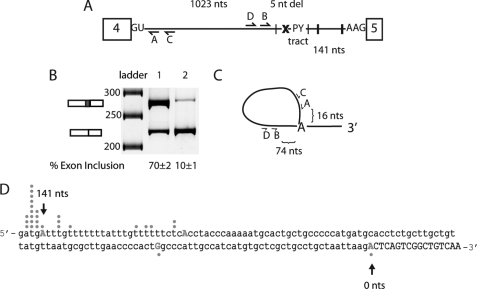
FIGURE 2.
Determination of branch point of intron 4 in MBNL1 pre-mRNA. A, schematic of the MBNL1 pre-mRNA showing the predicted MBNL1 binding sites (black hatch marks indicate instances of YGCY motifs); the x represents the deletion of the predicted branch point (ATGAT) in intron 4. The minigene containing the deletion of the predicted branch point was termed Δbp. The locations of the four primers used for branch point mapping are shown (A–D). B, splicing of the wild type and Δbp minigene. Lane 1 contains the wild type MBNL1 minigene, and lane 2 contains the Δbp minigene. C, schematic representation of the primers used for the RT-PCR to isolate lariats. Primer C was used for RT-PCR, primer pairs C and D were used for the initial PCR, and primer pairs A and B were used for the final nested PCR. Distances between primer B and the distant branch point and primer A and the distant branch point are shown. D, sequence for the 3′-end of intron 4 (in lowercase) and part of exon 5 (capitalized) are shown. 145 nucleotides of intronic region upstream exon 5 are shown, and the first 17 nucleotides of exon 5 are shown. Dots correlate with the number of clones for the lariats that were sequenced to the particular nucleotide. The first position in the exon is numbered zero (0) with upstream nucleotides being negative and downstream nucleotides from the first nucleotide of the exon being positive. nt(s), nucleotide(s).