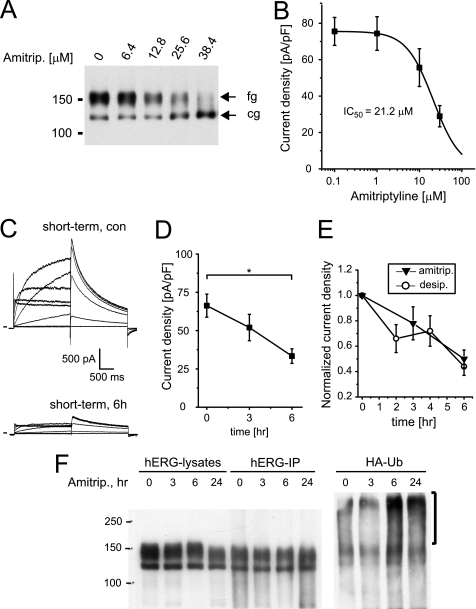
FIGURE 13.
Amitriptyline increases hERG ubiquitination. A, Western blot shows the effects of overnight incubation with increasing concentrations of amitriptyline on hERG protein stably expressed in HEK293 cells. Equal amounts of protein were loaded; fg indicates the fully glycosylated, 150-kDa cell surface form of hERG; cg indicates the core-glycosylated, 135-kDa ER-resident form of hERG. B, shown are the concentration-dependent effects on hERG tail currents after overnight exposure to amitriptyline. IC50 is 21.2 μm (n = 7–13). C, representative hERG current families recorded under control conditions or after a 6-h exposure to 30 μm amitriptyline are shown. Currents were elicited using depolarizing voltage steps from −60 to +60 mV. Tail currents were recorded on return to −50 mV. Holding potential was −80 mV. D, time-dependent reduction of hERG tail current densities recorded on exposure to 30 μm amitriptyline (n = 9–10) is shown. Note that current density at t = 6 h is significantly different from control, Dunnett's, p < 0.05. E, normalized time-dependent changes in tail current levels recorded in the presence of either 30 μm desipramine or 30 μm amitriptyline (amitrip) are shown. F, shown is a Western blot analysis of HEK/hERG cells transiently transfected with HA-tagged ubiquitin and treated for 3 and 6 h or overnight (24 h) with 30 μm amitriptyline. Whole cell lysates, shown in the right part of panel, were immunoprecipitated with anti-hERG antibody, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and immunoblotted using either anti-hERG antibody (hERG-IP) or an antibody recognizing the HA epitope fused to ubiquitin (HA-Ub). Immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody identifies high molecular weight forms of ubiquitinated hERG that are increased on 6- and 24-h exposure to 30 μm desipramine. Data are given as the mean ± S.E.