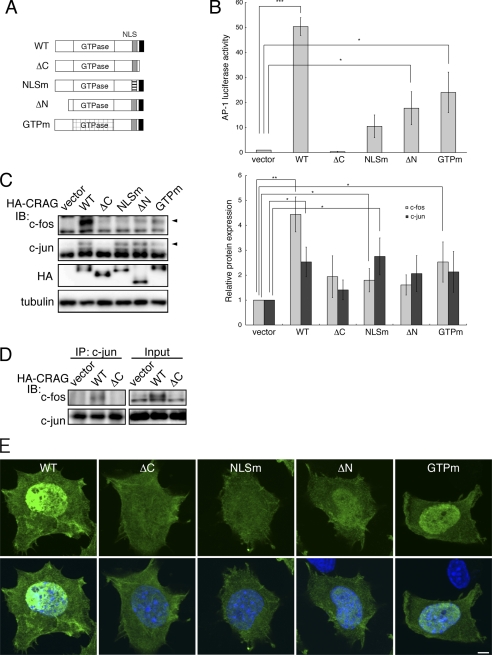
FIGURE 2.
Identification of CRAG domains required for AP-1 activation. A, structural comparison of CRAG wild-type (WT) with various CRAG mutants. WT, CRAG WT; ΔC, CRAGΔC 1–374 mutant; NLSm, CRAG NLS mutant K386E R369E; ΔN, CRAGΔN 60–375 mutant; GTPm, CRAG GTPase mutant. B, AP-1 activities in cells expressing CRAG WT and mutants. Neuro2A cells were transfected with both pAP-1-Luc and pRL-CMV together with either empty expression vector or each indicated vector. Luciferase activities were assessed 48 h after the transfection. Error bars indicate ±S.D. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.005 (Student's t test). C, effects of CRAG mutants on activations of c-Fos and c-Jun. Lysates of Neuro2A cells as described above were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Arrowheads indicate the positions of phosphorylated c-Fos and c-Jun. The protein levels of c-Fos and c-Jun normalized with tubulin are shown in the right panel when the control value was arbitrarily set 1.0. Error bars indicate ±S.D. (n = 4). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. D, CRAG induces the formation of c-Fos/c-Jun heterodimer. Co-immunoprecipitation assay was performed on cells expressing vector, CRAG WT, or CRAGΔC. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-c-Jun antibody, and the immunoprecipitates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. E, subcellular localizations of CRAG WT and mutants. Neuro2A cells as described above were immunostained with anti-HA (green) antibody and Hoechst 33258 (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm.