FIGURE 6.
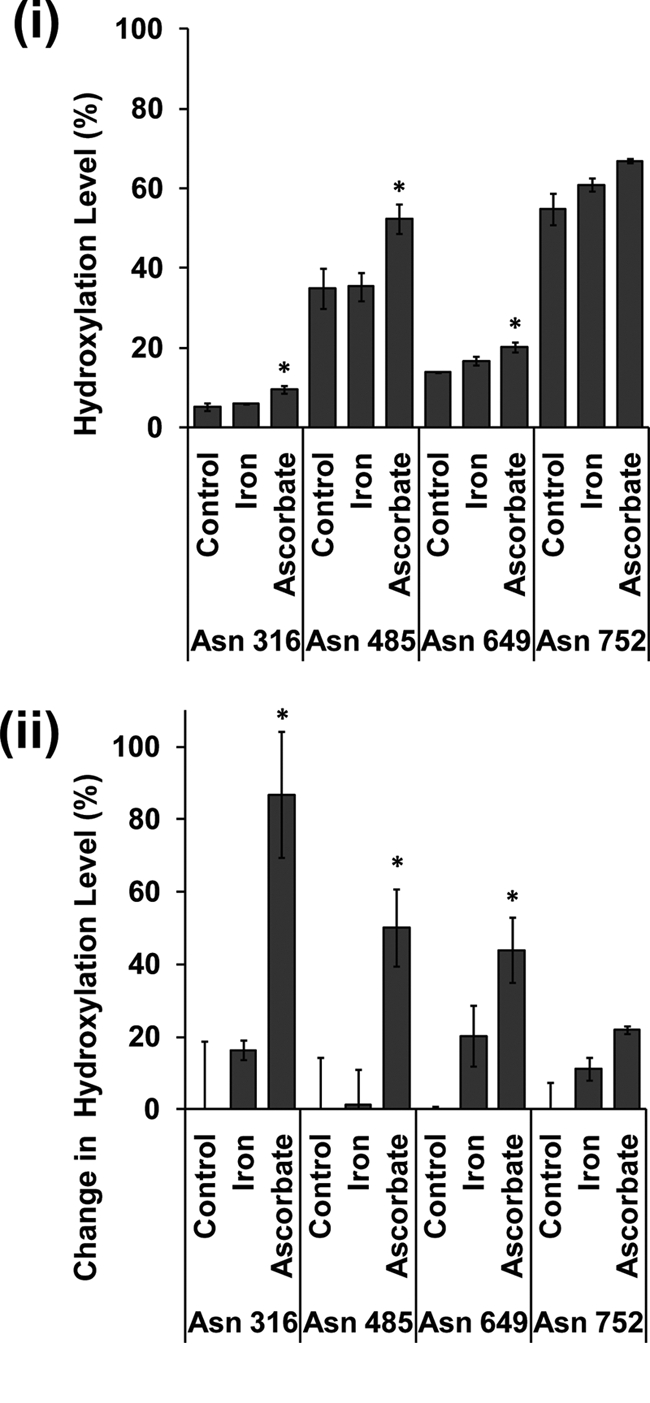
Effect of ferrous iron and l-ascorbate supplementation on FIH-dependent hydroxylation of Rabankyrin-5. Heavy SILAC media were added to cells stably expressing FLAG-tagged Rabankyrin-5 at the time of iron (40 μm) and ascorbate (50 μm) supplementation. Heavy labeled peptides encompassing known hydroxylation sites were quantified by LC-MS/MS. Data presented are from three independent biological replicates (mean ± S.E.); peptide loss was observed for Asn316, Asn649, Asn752 (n = 2). i shows the level of hydroxylation; ii, illustrates the change in the level of hydroxylation at named sites following co-factor addition. This value is derived from ((level in test condition − level in control condition)/level in control condition) × 100. *, p < 0.05 compared with control by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnett's test (n = ≥2).
